Lichen: Difference between revisions
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Types of Lichen= | =Types of Lichen= | ||
Lichen occur in one of four main growth forms | Lichen occur in one of four main growth forms: (5) | ||
- ''Crustose lichen'' are lichen that are pressed against their substrate. They form a crust over their substrate. (6) Their medulla is in direct contact with the substrate it is growing on. (7) | |||
''Crustose lichen'' are lichen that are pressed against their substrate. They form a crust over their substrate. (6) Their medulla is in direct contact with the substrate it is growing on. (7) | |||
[[File:Crustose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Crustose Lichen (7)]] | [[File:Crustose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Crustose Lichen (7)]] | ||
''Squamulose lichen'' are lichen with thallus that is small, flat, usually massed with overlapping scales, or squamules. (7) | - ''Squamulose lichen'' are lichen with a thallus, or a body that is not separated into stem and leaves, that is small, flat, and usually massed with overlapping scales, or squamules. (7) | ||
[[File:Squamulose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Squamulose Lichen (7)]] | [[File:Squamulose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Squamulose Lichen (7)]] | ||
''Foliose lichen'' are lichen with a thallus that generally | - ''Foliose lichen'' are lichen with a thallus that generally form flat, leaf-like lobes with differentiated layers of tissue. The lower cortex is typically a different color and usually has rhizines to attach to it's substrate. (7) | ||
[[File:Foliose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Foliose Lichen (7)]] | [[File:Foliose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Foliose Lichen (7)]] | ||
''Fruticose Lichen'' are lichen with a thallus that is extended up into a tufted or pendant branched structure. (7) They are free-standing branched tubes.(5) | - ''Fruticose Lichen'' are lichen with a thallus that is extended up into a tufted or pendant branched structure. (7) They are free-standing branched tubes.(5) | ||
[[File:Fruticose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Fruticose Lichen (7)]] | [[File:Fruticose lichen.jpg|right|thumb|Fruticose Lichen (7)]] | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 2 May 2019
Lichen is a compound organism, made up of two species. A fungus and a cyanobacteria or green algae live symbiotically, and both are benefited from this mutualistic relationship. The most common types of cyanobacteria are Nostoc or Scytonema. The most common types of green algaes in lichen are pleurastrophycean green alga, such as Trebouxia, Pseudotrebouxia, or Myrmec. The fungi is either an Ascomycete or a Basidiomycete. (10) In exchange for a safe habitat to live in, the cyanobacteria or green algae provide food to the fungus from their photosynthetic processes. (1)There are as many as 20,000 known lichen organisms, and new ones being discovered often. (10)
Types of Lichen
Lichen occur in one of four main growth forms: (5)
- Crustose lichen are lichen that are pressed against their substrate. They form a crust over their substrate. (6) Their medulla is in direct contact with the substrate it is growing on. (7)

- Squamulose lichen are lichen with a thallus, or a body that is not separated into stem and leaves, that is small, flat, and usually massed with overlapping scales, or squamules. (7)

- Foliose lichen are lichen with a thallus that generally form flat, leaf-like lobes with differentiated layers of tissue. The lower cortex is typically a different color and usually has rhizines to attach to it's substrate. (7)

- Fruticose Lichen are lichen with a thallus that is extended up into a tufted or pendant branched structure. (7) They are free-standing branched tubes.(5)

Biology
Unlike plants, lichen do not have a vascular system. This means they do not have a xylem or phloem to move nutrients and water around their plant body. Lichen get their water and nutrients by absorbing them from their surroundings. (3) The majority of the lichen's body is formed by filaments from the fungal body, and the varying density of these filaments defines the layers of the lichen. (5)

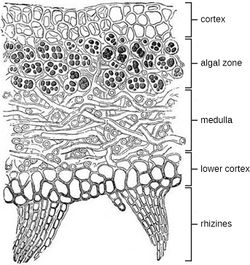
Cortex
The outer layer of the lichen is called the cortex. The filaments in the cortex are thicker and more closely packed, providing a small amount of protection for the organism. (3) The densely packed filaments also helps to reduce the intensity of light, which can cause damage to the alga cells. (5)
Symbiont Layer
Below the cortex, the fungal filaments are not so dense. This is the layer where the aglal cells are distributed. (5) This is the layer than photosynthesis occurs in.
Medulla
Fungal filaments, or medulla, make up most of the lichen organism. Fungal cells are loosely packed in the middle of the lichen body, with thin cell walls and a threadlike structure. (3)
Attachments
Rhizines
Some lichen use rhizines to attach to their substrate. Rhizines are fungal filaments extending out from the medulla. Rhizines do not move water or help the lichen breathe. Their sole purpose is stabilizing the lichen down. (3)
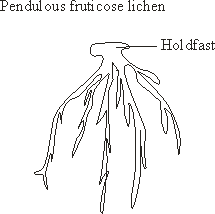
Holdfast
Some lichen use holdfasts to fasten themselves down. This is a central peg that extends out from the lichen thallus. (3)
Ecology
Lichen play a huge role in the development of ecosystems, and also a huge role in established ecosystems. They play an important role in the water cycle in forests, greatly increasing the interception and absorption of precipitation. (4) Lichen are able to sequester limiting nutrients from the atmosphere, and these in turn become available to other organisms when lichen die, fall, and decompose, or through leachate. (4) The presence of lichen also provides increased habitat complexity for small organisms. There is a close relationship between lichen and invertebrates, including Arachnids such as orabitid mites, insects, rotifers, tardigrades, and spiders. (4) Providing habitat for these micro organisms is the base of the food chain, and provides food sources for the rest of the food web.
Pioneer Species
Lichen are considered pioneer species, or the first organism to appear in areas of primary succession. (2) They are able to colonize bare rocks, and an ecosystem is then able to begin developing on them. The fungal partner in the lichen releases chemicals that break down rock minerals, which are then able to be consumed by the algal partner. (11)
Indication
An indicator species is a species that tells something about the environment by their presence, or absence, in that environment. Lichens are indicators of environmental pollution. They have no way to detoxify and excrete harmful chemicals from the air, so absence of lichen in an ecosystem can be an indicator of environmental stress due to pollution. (1)
References
[1] Lewis, Ricki. "Lichen." Biology, edited by Melissa Sue Hill, 2nd 2d., vol. 3, Macmillan Reference USA, 2016, pp 12-13. Science in Context
[2] Discovery Education Science, Primary and Secondary Succession
[3] “Lichen Biology.” Lichen Biology - Structure, www.fs.fed.us/wildflowers/beauty/lichens/biology/index.shtml.
[4] Ellis, Christopher J. “Lichen Epiphyte Diversity: A Species, Community and Trait-Based Review.” Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, vol. 14, no. 2, 2012, pp. 131–152., doi:10.1016/j.ppees.2011.10.001.
[5] http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fungi/lichens/lichenmm.html
[6] “Lichen Biology.” US Forest Service, www.fs.fed.us/wildflowers/beauty/lichens/biology/growthforms.shtml.
[7] http://www.lichens.lastdragon.org/faq/lichenthallustypes.html
[8] https://courses.lumenlearning.com/microbiology/chapter/lichens/
[9] http://resizing.info/imgeditor.html
[10] Lichens: Systematics. Berkeley.edu, www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fungi/lichens/lichensy.html.
[11] “Soil Genesis and Development, Lesson 2 - Processes of Weathering.” Plant and Soil Sciences ELibrary, passel.unl.edu/pages/informationmodule.php?idinformationmodule=1124303183&topicorder=5&maxto=6.