Alfisols: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (<a rel="nofollow" class="external free" href="https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles">https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles</a>). |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Alfisols are latitudinally the most widespread of the twelve [[soil]] orders defined by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) [3] | Alfisols are mildly acidic soils with significant accumulation of clays, possessing a soil moisture regime that is moist for most of the year [6]. These are latitudinally the most widespread of the twelve [[soil]] orders defined by the United States Department of [[Agriculture]] (USDA) [3]. Alfisols are typically well-drained and commonly used for agriculture. | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Alfisols are found in a variety of climates around the world. Some areas where they are prominent include West Africa immediately south of the Sahara Desert, eastern India, much of Europe and western Russia, the Midwest and Great Lakes regions of the United States, parts of the Australia coastline, and various other areas of the world [5]. | Alfisols are found in a variety of climates around the world. Some areas where they are prominent include West Africa immediately south of the Sahara Desert, eastern India, much of Europe and western Russia, the Midwest and Great Lakes regions of the United States, parts of the Australia coastline, and various other areas of the world [5]. | ||
The distribution of alfisols often forms a buffer between other soil orders with differing soil moisture regimes [5]. In warm climates they can occur adjacent to [[ | The distribution of alfisols often forms a buffer between other soil orders with differing soil moisture regimes [5]. In warm climates they can occur adjacent to [[aridisols]] (dry soils), separating them from various other soil orders associated with humid climates. An example where this occurs is in Texas, where alfisols in central and east Texas separate the dry West Texas soils from the humid southeastern United States. In mesic or cool climates Alfisols often occur adjacent to Mollisols (grassland soils). | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
Diagnostic features of alfisols include a thin ochric epipedon, which is a light-colored surface horizon, and a prominent argillic horizon [2]. The argillic horizon is a product of silicate [[clay]] accumulation in the B horizon via illuviation, and cation exchange capacity in this horizon is over 35% saturated with base-forming cations [2]. Soil water potential greater than 1500 kPa is considered a “moist” soil moisture regime, and alfisols typically exceed this for most of the year, although for at least 3 months of the year soil moisture in alfisols falls below this threshold [ | Diagnostic features of alfisols include a thin ochric epipedon, which is a light-colored surface horizon (see: [[Soil Horizons]]), and a prominent argillic horizon [2]. The argillic horizon is a product of silicate [[clay]] accumulation in the B horizon via illuviation, and cation exchange capacity in this horizon is over 35% saturated with base-forming cations [2]. Soil water potential greater than 1500 kPa is considered a “moist” soil moisture regime, and alfisols typically exceed this for most of the year, although for at least 3 months of the year soil moisture in alfisols falls below this threshold [6]. | ||
[[File:Alfisol soil profile.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Alfisol soil profile [https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/survey/class/maps/?cid=nrcs142p2_053590]]] | [[File:Alfisol soil profile.jpg|200px|thumb|left|Alfisol soil profile [https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/survey/class/maps/?cid=nrcs142p2_053590]]] | ||
Temperate forests and cropland commonly occur on alfisols, and net primary productivity is usually high. In some areas, particularly eastern Europe/western Russia and the Midwestern United States, there is substantial occurrence of loess [3]. Loess refers to the depositional products of [[soil erosion]] by wind. These soils are generally very fertile, as evidenced by the loess deposits in the intensively cultivated Midwestern United States. | Temperate forests and cropland commonly occur on alfisols, and net primary productivity is usually high. In some areas, particularly eastern Europe/western Russia and the Midwestern United States, there is substantial occurrence of loess [3]. Loess refers to the depositional products of [[soil erosion]] by wind. These soils are generally very fertile, as evidenced by the loess deposits in the intensively cultivated Midwestern United States. | ||
== Distribution of Suborders in the United States == | == Distribution of Suborders in the United States == | ||
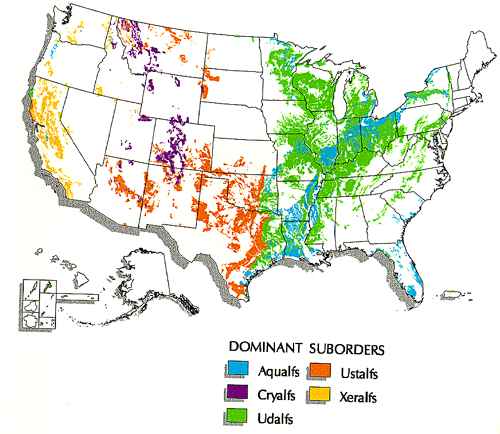
Five suborders of alfisols occur in the United States, comprising 13.9% of land area in the U.S. [10]: | |||
Aqualfs- often cultivated for common crops including corn, rice, and soybeans. | Aqualfs- often cultivated for common crops including corn, rice, and soybeans. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
[[File:AlfisolsSuborders.jpeg | ]] | [[File:AlfisolsSuborders.jpeg | ]] | ||
Suborder information and map from | |||
Suborder information and map from USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service [10] | |||
== Ecology == | == Ecology == | ||
Around the world, alfisols are used intensively for agriculture. In the United States, particularly the Midwest and Great Lakes regions, major crops include grains, corn, and hay [3]. Dairy farming is also common in these areas. Alfisols in Mediterranean climates (i.e. Europe and California) are cultivated for fruits, nuts, and various specialty crops such as olives [3]. An important process that occurs in alfisol agroecosystems is crop straw [[decomposition]], which increases soil organic matter and nutrient availability [6]. Alfisols that are low in organic matter are susceptible to soil erosion, particularly in agricultural areas [1]. A variety of best management practices for agriculture are utilized in these areas, such as crop rotations, cover cropping, and fallowing [1]. | Around the world, alfisols are used intensively for agriculture. In the United States, particularly the Midwest and Great Lakes regions, major crops include grains, corn, and hay [3]. Dairy farming is also common in these areas. Alfisols in Mediterranean climates (i.e. Europe and California) are cultivated for fruits, nuts, and various specialty crops such as olives [3]. An important process that occurs in alfisol agroecosystems is crop straw [[decomposition]], which increases soil [[Organic Matter|organic matter]] and nutrient availability [6]. Alfisols that are low in [[Organic Matter|organic matter]] are susceptible to soil erosion, particularly in agricultural areas [1]. A variety of best management practices for agriculture are utilized in these areas, such as crop rotations, cover cropping, and fallowing [1]. | ||
[[File:Enchytraeids.JPG|200px|thumb|left|Enchytraeids in soil [https://www.wur.nl/en/Research-Results/Chair-groups/Environmental-Sciences/Soil-Biology-Group/Research/The-Soil-Biota/Enchytraeids-potworms.htm]]] | [[File:Enchytraeids.JPG|200px|thumb|left|Enchytraeids in soil [https://www.wur.nl/en/Research-Results/Chair-groups/Environmental-Sciences/Soil-Biology-Group/Research/The-Soil-Biota/Enchytraeids-potworms.htm]]] | ||
The geographic and climatic [[diversity]] of alfisols means that a greater variety of flora and fauna exists compared to other soil orders. Astigmatic [[mites]] are often found at their greatest densities in agroecosystems after events that increase soil organic matter, such as harvest, tillage, and the application of soil amendments [ | The geographic and climatic [[diversity]] of alfisols means that a greater variety of flora and fauna exists compared to other soil orders. Astigmatic [[mites]] are often found at their greatest densities in agroecosystems after events that increase soil organic matter, such as harvest, tillage, and the application of soil amendments [8]. Enchytraeids are often found at higher densities in alfisols compared to other soils – they are typically associated with high acidity and organic matter found in temperate forests, grasslands, and agricultural areas [4,11]. In forested and cultivated alfisols, enchytraeid populations typically occur in the upper soil horizons where organic matter is highest, but may be found at greater depths in grasslands soils (usually mollisols) [4,5].Other prominent soil fauna in agroecosystems include Carabidae (ground beetles) and various species of mound-building and humivorous [[termites]] [9]. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 52: | ||
[4]Coleman, David C., Callaham Jr., Mac A., and Crossley Jr., D. A. “Fundamentals of [[Soil Ecology]], Third Edition.” 2018. Academic Press. Cambridge, MA. | [4]Coleman, David C., Callaham Jr., Mac A., and Crossley Jr., D. A. “Fundamentals of [[Soil Ecology]], Third Edition.” 2018. Academic Press. Cambridge, MA. | ||
[5]Soil Taxonomy, Second Edition. 1999. United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service. pg. 163. | [5]Davidson, D.A., Bruneau, P.M.C., Grieve, I.C., and Young, I.M. Impacts of fauna on an upland grassland soil as determined by micromorphological analysis. 2002. Applied Soil Ecology. 20:133-143. | ||
[6]Soil Taxonomy, Second Edition. 1999. United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service. pg. 163. | |||
[7]Li, Ji-Fu, and Zhong, Fang-Fang. Nitrogen release and re-adsorption dynamics on crop straw residue during straw decomposition in an Alfisol. 2021. Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 20(1):248–259. | |||
[8]Perdue, J.C., and Crossley Jr., D.A. Seasonal abundance of soil mites ([[Acari]]) in experimental agroecosystems: effects of drought in no-tillage and conventional tillage. 1989. Soil Tillage Res. 15:117-124. | |||
[9]Purvis, G., and Fadel, A. The influence of cropping rotations and soil cultivation practice on the population ecology of carabids ([[Coleoptera]], Carabidae) in arable land. 2002. Pedobiologia. 46:452-474. | |||
[ | [10]USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. Alfisols Map. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/survey/class/maps/?cid=nrcs142p2_053591 | ||
[ | [11]van Vliet, P.C.J., West, L.T., Hendrix, P.F., and Coleman, D.C. The influence of [[Enchytraeidae]] (Oligochaeta) on the soil [[porosity]] of small microcosms. 1993. Geoderma. 56:287-299. | ||
Revision as of 12:30, 17 June 2024
Alfisols are mildly acidic soils with significant accumulation of clays, possessing a soil moisture regime that is moist for most of the year [6]. These are latitudinally the most widespread of the twelve soil orders defined by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) [3]. Alfisols are typically well-drained and commonly used for agriculture.
Definition
Alfisols are found in a variety of climates around the world. Some areas where they are prominent include West Africa immediately south of the Sahara Desert, eastern India, much of Europe and western Russia, the Midwest and Great Lakes regions of the United States, parts of the Australia coastline, and various other areas of the world [5].
The distribution of alfisols often forms a buffer between other soil orders with differing soil moisture regimes [5]. In warm climates they can occur adjacent to aridisols (dry soils), separating them from various other soil orders associated with humid climates. An example where this occurs is in Texas, where alfisols in central and east Texas separate the dry West Texas soils from the humid southeastern United States. In mesic or cool climates Alfisols often occur adjacent to Mollisols (grassland soils).
Description
Diagnostic features of alfisols include a thin ochric epipedon, which is a light-colored surface horizon (see: Soil Horizons), and a prominent argillic horizon [2]. The argillic horizon is a product of silicate clay accumulation in the B horizon via illuviation, and cation exchange capacity in this horizon is over 35% saturated with base-forming cations [2]. Soil water potential greater than 1500 kPa is considered a “moist” soil moisture regime, and alfisols typically exceed this for most of the year, although for at least 3 months of the year soil moisture in alfisols falls below this threshold [6].

Temperate forests and cropland commonly occur on alfisols, and net primary productivity is usually high. In some areas, particularly eastern Europe/western Russia and the Midwestern United States, there is substantial occurrence of loess [3]. Loess refers to the depositional products of soil erosion by wind. These soils are generally very fertile, as evidenced by the loess deposits in the intensively cultivated Midwestern United States.
Distribution of Suborders in the United States
Five suborders of alfisols occur in the United States, comprising 13.9% of land area in the U.S. [10]:
Aqualfs- often cultivated for common crops including corn, rice, and soybeans.
Ustalfs- occur mainly in the Great Plains and Rocky Mountains in semiarid climates.
Cryalfs- found at higher elevations, particularly in the Rocky Mountains. Often forested due to cool climate and short growing season.
Xeralfs- found on the west coast, often used as cropland or pastureland.
Udalfs- udic soil moisture regime, found in humid climates.
Suborder information and map from USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service [10]
Ecology
Around the world, alfisols are used intensively for agriculture. In the United States, particularly the Midwest and Great Lakes regions, major crops include grains, corn, and hay [3]. Dairy farming is also common in these areas. Alfisols in Mediterranean climates (i.e. Europe and California) are cultivated for fruits, nuts, and various specialty crops such as olives [3]. An important process that occurs in alfisol agroecosystems is crop straw decomposition, which increases soil organic matter and nutrient availability [6]. Alfisols that are low in organic matter are susceptible to soil erosion, particularly in agricultural areas [1]. A variety of best management practices for agriculture are utilized in these areas, such as crop rotations, cover cropping, and fallowing [1].

The geographic and climatic diversity of alfisols means that a greater variety of flora and fauna exists compared to other soil orders. Astigmatic mites are often found at their greatest densities in agroecosystems after events that increase soil organic matter, such as harvest, tillage, and the application of soil amendments [8]. Enchytraeids are often found at higher densities in alfisols compared to other soils – they are typically associated with high acidity and organic matter found in temperate forests, grasslands, and agricultural areas [4,11]. In forested and cultivated alfisols, enchytraeid populations typically occur in the upper soil horizons where organic matter is highest, but may be found at greater depths in grasslands soils (usually mollisols) [4,5].Other prominent soil fauna in agroecosystems include Carabidae (ground beetles) and various species of mound-building and humivorous termites [9].
References
[1]Adekiya, A.O., and others. Soil productivity improvement under different fallow types on Alfisol of a derived savanna ecology of Nigeria. 2021. Heliyon. 7:e06759.
[2]Brady, Nyle C., and Weil, Ray R. “Elements of the Nature and Properties of Soils.” 2000. Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, NJ.
[3]Christopherson, Robert W. “Geosystems: An Introduction to Physical Geography, Tenth Edition.” 2017. Pearson. Hoboken, NJ.
[4]Coleman, David C., Callaham Jr., Mac A., and Crossley Jr., D. A. “Fundamentals of Soil Ecology, Third Edition.” 2018. Academic Press. Cambridge, MA.
[5]Davidson, D.A., Bruneau, P.M.C., Grieve, I.C., and Young, I.M. Impacts of fauna on an upland grassland soil as determined by micromorphological analysis. 2002. Applied Soil Ecology. 20:133-143.
[6]Soil Taxonomy, Second Edition. 1999. United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service. pg. 163.
[7]Li, Ji-Fu, and Zhong, Fang-Fang. Nitrogen release and re-adsorption dynamics on crop straw residue during straw decomposition in an Alfisol. 2021. Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 20(1):248–259.
[8]Perdue, J.C., and Crossley Jr., D.A. Seasonal abundance of soil mites (Acari) in experimental agroecosystems: effects of drought in no-tillage and conventional tillage. 1989. Soil Tillage Res. 15:117-124.
[9]Purvis, G., and Fadel, A. The influence of cropping rotations and soil cultivation practice on the population ecology of carabids (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in arable land. 2002. Pedobiologia. 46:452-474.
[10]USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. Alfisols Map. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/survey/class/maps/?cid=nrcs142p2_053591
[11]van Vliet, P.C.J., West, L.T., Hendrix, P.F., and Coleman, D.C. The influence of Enchytraeidae (Oligochaeta) on the soil porosity of small microcosms. 1993. Geoderma. 56:287-299.