Difference between revisions of "Loam"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Physical Properties== | ==Physical Properties== | ||
[[File:Soil texture triangle.png|thumb|Photo courtesy of USDA Horticulture and soil science wiki]] | [[File:Soil texture triangle.png|thumb|Photo courtesy of USDA Horticulture and soil science wiki]] | ||
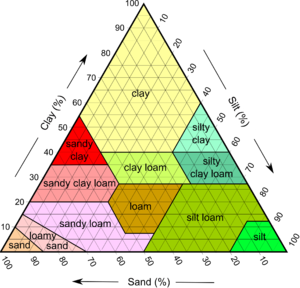
| − | As seen in the figure to the right, the three types of soil can be combined in different amounts to form varying types of loam. The particle sizes range from large to small starting with sand, which is defined as having a particle size greater than 63 µm, silt, with a particle size greater than 2 µm, and clay, with particle sizes smaller than 2 µm. [1] | + | As seen in the figure to the right, the three types of soil can be combined in different amounts to form varying types of loam. The particle sizes range from large to small starting with sand, which is defined as having a particle size greater than 63 µm, silt, with a particle size greater than 2 µm, and clay, with particle sizes smaller than 2 µm. [1] Loamy soil is the soil type most likely to contain an ample amount of humus, or dead organic matter from plants and animals, that fosters plant growth. |
==Life within the soil== | ==Life within the soil== | ||
Revision as of 11:19, 20 April 2018
Loam is a type of soil comprised of varying proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
Physical Properties
As seen in the figure to the right, the three types of soil can be combined in different amounts to form varying types of loam. The particle sizes range from large to small starting with sand, which is defined as having a particle size greater than 63 µm, silt, with a particle size greater than 2 µm, and clay, with particle sizes smaller than 2 µm. [1] Loamy soil is the soil type most likely to contain an ample amount of humus, or dead organic matter from plants and animals, that fosters plant growth.
Life within the soil
Some of the inhabitants of loamy soil include the water-dependent protozoa and nematoda. They usually prefer soil containing more silt than sand due to its tendency to hold water. [2] Acari, also known as mites, can tolerate more desiccation than other microorganisms, so they do not need as much exposure to water and can live in a larger range of soil types.
Fertility of loamy soil
Loam is the best-suited soil type for growing most plants due to its propensity for holding enough water and nutrients to satisfy their needs. [3] Clay dominant soils, although rich in nutrients, have poor drainage due to the small pore size and is not ideal for roots to grow in. Sandy soils do not hold water well, and silt does not hold nutrients well. These characteristics mixed together end up forming fertile loam, the ideal soil type for many plant types.
Specifically, loamy soil is the preferred growing environment for plants such as strawberries, corn, sunflowers, beets, kale, lettuce, mint, sweet potatoes, peas, tomatoes, and turnips, among others. [4]
References
[1] Kaufmann, Robert K.; Cutler J. Cleveland (2008). Environmental Science. McGraw-Hill. pp. 318–319. ISBN 978-0-07-298429-3.
[2] Coleman, D. C., Crossley, D. A., Jr., & Hendrix, P. F. (2004). Fundamentals of Soil Ecology (2nd ed.). Amstherdan: Elsevier.
[3] R. B. Brown (September 2007). "Soil Texture" (PDF). Agronomy Fact Sheet Series: Fact Sheet SL-29. Cornell University, Department of Crop and Soil Sciences. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
[4] Old Farmer's Almanac. “Soil Type: Loamy.” Old Farmer's Almanac, www.almanac.com/plants/soil/loamy.