Lignin
Description
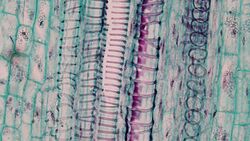
Lignin is a complex polymer found in the cell walls of many plant species. Lignin is especially important in the formation of cell walls in rigid and woody plant species. Lignin is incredibly rigid, allowing tree species to grow tall, while also allowing for movement of the branches in the presence of stressors such as wind and animal inhabitance. Lignin also aids in the transportation of water and minerals throughout the organism [1]. Lastly, it provides the plant with mechanisms that resist damage from pathogens and invading pests. All plants containing lignin are called tracheophytes, which have a vascular system of roots, leaves, and stems. Plants without lignin are called bryophytes and are non-vascular with no roots, leaves, or stems [2].
Structure
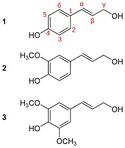
Lignin is formed by the crossing of lignols. There are three main types of lignols; conyferal alcohol, sinapyl alcohol, and paracoumaryl alcohol. These lignols are found in all plant species containing lignin, however their abundance will change according to the rigidity and type of the wood they are found in [3]. Hardwoods have a higher abundance of conyferal alcohol and sinapyl alcohol, while softwoods are more rich in conyferal alcohol, and grasses have a higher abundance of sianpyl units. The higher the concentration of lignin of any kind will result in a more rigid material.


Ecological Importance
Lignin plays a crucial role in the carbon cycle. Lignin absorbs atmospheric carbon and holds it within the plant tissue. It also is one of the slowest decomposing materials of a dead tree, becoming a very high fraction of the production of humus and top soil. Only a small amount of organisms are able to decompose lignin. Fungi are known to be the greatest decomposers of lignin since they have the ability produce an extracellular peroxidase that can kick start the decomposition of the material [4].
Lignin fills in the extracellular space between cellulose and hemicellulose and pectin creating a dense, rigid structure to support the plant. In edition to providing rigidity and support, lignin also aids in the transport of water through the plant. while a plants leaf tissue can easily absorb water, lignin is hydrophobic. Its presence in the tissue of the leaves acts as a barrier, slowing down the absorption of water allowing the plant to transport it more efficiently [5].
References
[1] Bodo, S., & Lehnen, R. (July 2007). "Lignin". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_305.pub3
[2] Jing-Ke W., Xu, L., Stout, J., Chappel, C. (June 2008). "Independent origins of syringyl lignin in vascular plants". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801696105
[3] Boerjan, W., Ralph, J., Baucher, M. (June 2003). "Lignin biosynthesis". Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 54 (1): 519–549. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134938
[4] Gadd, G., Sariaslani, S. (March 2013). Advances in applied microbiology. Vol. 82. Oxford: Academic. pp. 1–28. ISBN 9780124076792. OCLC 841913543
[5] Sarkanen, K. V., & Ludwig, C. H. (eds) (March 1972). "Lignins: Occurrence, Formation, Structure, and Reactions". Journal of Polymer Science New York: Wiley Interscience. doi:10.1002/pol.1972.110100315