Red Velvet Ant: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[[File:Cicada Killer Wasp MF.jpg|frame|center | Male vs Female Eastern Cicada Killer]] | [[File:Cicada Killer Wasp MF.jpg|frame|center | Male vs Female Eastern Cicada Killer]] | ||
Red Velvet Ants are in the Miltillidae family, which holds 7000 different species of velvet ants. Despite their name and appearcance, Red Velvet Ants are actually a species of wasp. Like most wasp species, they are solitary and do not form larger hives. These wasps get their name from their short, red and black, velvety hairs covering their body. | Red Velvet Ants are in the Miltillidae family, which holds 7000 different species of velvet ants. Despite their name and appearcance, Red Velvet Ants are actually a species of wasp. Like most wasp species, they are solitary and do not form larger hives. These wasps get their name from their short, red and black, velvety hairs covering their body. On top of their aposmatic coloration, females can also produce a squeaking sound to warn off predators. Red velvet Ants are the largest of the velvet ant species, measuring about 3/4 of an inch in length. Females are wingless while males have dark, transulucent wings. The females wingless appareance and the way they move acroos the ground is why these insects are mistaken as ants. Females also posses a stinger, while males do not. These wasps are also known as "Cow Killers" due to their quite powerful and painful sting. | ||
== Habitat and Range == | == Habitat and Range == | ||
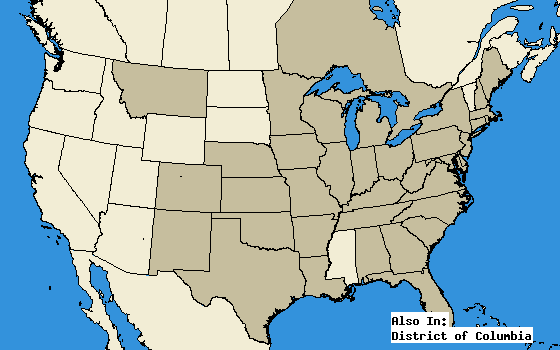
Red Velvet Ants are native to North America. Their main range is the eastern United States. In the north, the range is conecticut to missouri, while in the south its florida to texas. They are often found in open, dry, and sandy areas with a lot of sun. Red velvet Ants are parasites and rely on host species for their repodcution style. Because of this they tend to be found in the same areas where ground nesting wasps and bees can live. | |||
[[File:Eastern-Cicada_Killer-Range.png|frame|right| [https://bugguide.net/node/view/514/data US Range of Eastern Cicada Killer]]] | [[File:Eastern-Cicada_Killer-Range.png|frame|right| [https://bugguide.net/node/view/514/data US Range of Eastern Cicada Killer]]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
== Behavior and Life Cycle == | == Behavior and Life Cycle == | ||
[[File:Cicada-killer-with-insect.jpg |1000px| thumb|right | [https://pamlico.ces.ncsu.edu/2024/08/cicada-killer-wasp/ Cicada caught by Eastern Cicada Killer]]] | [[File:Cicada-killer-with-insect.jpg |1000px| thumb|right | [https://pamlico.ces.ncsu.edu/2024/08/cicada-killer-wasp/ Cicada caught by Eastern Cicada Killer]]] | ||
Red Velvet Ants are solitary and do not from eusoical hives like hornets do. They are dinural and rest during the night. Adults feed on nectar from plants, while their young are strictly parasitc. They are generally non aggresive and will not attck other species outside of their reproductive cycle. The only time a Red Velvet Ant comes into contact with one another is to mate. | |||
They begin reproducing in the warmer months of the year. Females tend to be seen scurrying across open fields whiel males fly in the air in search of a mate. Once males locate a femlae through pheromones or hearing females squeaking, they pick the female up with their mandibles and fly awya. The males will then find a spot deemed safe to mate, typically in a shaded area and away from other competitors. Once the process is over, the female will then begin to look for suitable hosts to lay their eggs. Red Velvet Ants host on numerous different species of ground bees and wasps. The most common host they use are wasps of Crabronidae such as Eastern Cicada Killers and Horse Guard Wasps. Once they locate the ground nest of a host, they will lay a single egg in one of the nests chambers and then leave. It is belive that these wasps mate only once in their lifetime. | |||
Roughly 3 days after being laid, the egg will hatch. The Red Velvet Ant larvae will then being to eat the larvae or pupae of the host species. It will feed until it is ready to enter its pupal stage. The pupal stage typically takes around 20 days to complete | |||
Revision as of 23:58, 18 April 2025

| |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
|---|---|
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Mutillidae |
| Genus: | Dasymutilla |
| Species: | Dasymutilla occidentalis |
Description

Red Velvet Ants are in the Miltillidae family, which holds 7000 different species of velvet ants. Despite their name and appearcance, Red Velvet Ants are actually a species of wasp. Like most wasp species, they are solitary and do not form larger hives. These wasps get their name from their short, red and black, velvety hairs covering their body. On top of their aposmatic coloration, females can also produce a squeaking sound to warn off predators. Red velvet Ants are the largest of the velvet ant species, measuring about 3/4 of an inch in length. Females are wingless while males have dark, transulucent wings. The females wingless appareance and the way they move acroos the ground is why these insects are mistaken as ants. Females also posses a stinger, while males do not. These wasps are also known as "Cow Killers" due to their quite powerful and painful sting.
Habitat and Range
Red Velvet Ants are native to North America. Their main range is the eastern United States. In the north, the range is conecticut to missouri, while in the south its florida to texas. They are often found in open, dry, and sandy areas with a lot of sun. Red velvet Ants are parasites and rely on host species for their repodcution style. Because of this they tend to be found in the same areas where ground nesting wasps and bees can live.

Behavior and Life Cycle

Red Velvet Ants are solitary and do not from eusoical hives like hornets do. They are dinural and rest during the night. Adults feed on nectar from plants, while their young are strictly parasitc. They are generally non aggresive and will not attck other species outside of their reproductive cycle. The only time a Red Velvet Ant comes into contact with one another is to mate.
They begin reproducing in the warmer months of the year. Females tend to be seen scurrying across open fields whiel males fly in the air in search of a mate. Once males locate a femlae through pheromones or hearing females squeaking, they pick the female up with their mandibles and fly awya. The males will then find a spot deemed safe to mate, typically in a shaded area and away from other competitors. Once the process is over, the female will then begin to look for suitable hosts to lay their eggs. Red Velvet Ants host on numerous different species of ground bees and wasps. The most common host they use are wasps of Crabronidae such as Eastern Cicada Killers and Horse Guard Wasps. Once they locate the ground nest of a host, they will lay a single egg in one of the nests chambers and then leave. It is belive that these wasps mate only once in their lifetime.
Roughly 3 days after being laid, the egg will hatch. The Red Velvet Ant larvae will then being to eat the larvae or pupae of the host species. It will feed until it is ready to enter its pupal stage. The pupal stage typically takes around 20 days to complete
Ecological Role


