Gastropoda: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Partula.jpg|thumb|''Partula taeniata, a tree snail from Moorea, French Polynesia.''[https://ucmp.berkeley.edu/taxa/inverts/mollusca/gastropoda.php]] | [[File:Partula.jpg|thumb|''Partula taeniata, a tree snail from Moorea, French Polynesia.''[https://ucmp.berkeley.edu/taxa/inverts/mollusca/gastropoda.php]] | ||
== Background & Life History == | == Background & Life History == | ||
Gastropods are one of the most diverse animal groups, both in form and habitat. They are the largest group of mollusks with more than 62,000 described living species, and they comprise about 80% of all living mollusks. Estimates of total extant species range from 40,000 to over 100,000, but there may be as many as 150,000 species [5]. They have a long and rich fossil record from the Early Cambrian that shows periodic extinctions of subclades, followed by diversification of new groups. The Class Gastropoda includes | Gastropods are one of the most diverse animal groups, both in form and habitat. They are the largest group of mollusks with more than 62,000 described living species, and they comprise about 80% of all living mollusks. Estimates of total extant species range from 40,000 to over 100,000, but there may be as many as 150,000 species [5]. They have a long and rich fossil record from the Early Cambrian that shows periodic extinctions of subclades, followed by diversification of new groups. The Class Gastropoda includes snails, [[slugs]], limpets, and sea hares. Gastropods have figured prominently in paleobiologic and biological studies, and have served as study [[organisms]] in numerous evolutionary, biomechanical, ecological, physiological, and behavioral investigations [5]. | ||
Gastropods are mainly dioecious | Gastropods are mainly dioecious yet some forms are hermaphroditic. Hermaphroditic forms exchange bundles of sperm to avoid self-fertilization; copulation may be complex and in some species ends with each individual sending a sperm-containing dart into the tissues of the other [6]. Marine species have veliger larvae. Most aquatic gastropods are benthic and mainly epifaunal but some are planktonic [5]. | ||
== Ecology & Habitat == | == Ecology & Habitat == | ||
Revision as of 16:36, 14 March 2022

Background & Life History
Gastropods are one of the most diverse animal groups, both in form and habitat. They are the largest group of mollusks with more than 62,000 described living species, and they comprise about 80% of all living mollusks. Estimates of total extant species range from 40,000 to over 100,000, but there may be as many as 150,000 species [5]. They have a long and rich fossil record from the Early Cambrian that shows periodic extinctions of subclades, followed by diversification of new groups. The Class Gastropoda includes snails, slugs, limpets, and sea hares. Gastropods have figured prominently in paleobiologic and biological studies, and have served as study organisms in numerous evolutionary, biomechanical, ecological, physiological, and behavioral investigations [5].
Gastropods are mainly dioecious yet some forms are hermaphroditic. Hermaphroditic forms exchange bundles of sperm to avoid self-fertilization; copulation may be complex and in some species ends with each individual sending a sperm-containing dart into the tissues of the other [6]. Marine species have veliger larvae. Most aquatic gastropods are benthic and mainly epifaunal but some are planktonic [5].
Ecology & Habitat
Gastropods live in every conceivable habitat on Earth, having a worldwide distribution. They have adapted to almost every kind of existence on earth, having colonized nearly every available medium. They occupy all marine habitats ranging from the deepest ocean basins to the supralittoral, as well as freshwater habitats, and other inland aquatic habitats including salt lakes [3]. They are also the only terrestrial mollusks, being found in virtually all habitats ranging from high mountains to deserts and rainforest, and from the tropics to high latitudes. Some of the more familiar and better-known gastropods are terrestrial gastropods (the land snails and slugs). Some live in freshwater, but the majority of all named species of gastropods live in a marine environment. In habitats where there is not enough calcium carbonate to build a really solid shell, such as on some acidic soils on land, there are still various species of slugs, and also some snails with a thin translucent shell, mostly or entirely composed of the protein conchiolin [4].
Their feeding habits are extremely varied, although most species make use of a radula in some aspect of their feeding behavior. They include grazers, browsers, suspension feeders, scavengers, detritivores, and carnivores. Carnivory in some taxa may simply involve grazing on colonial animals, while others engage in hunting their prey. Some gastropod carnivores drill holes in their shelled prey. This method of entry has been acquired independently in several groups, as is also the case with carnivory itself. Some gastropods feed suctorially and have lost the radula [5].
Morphology
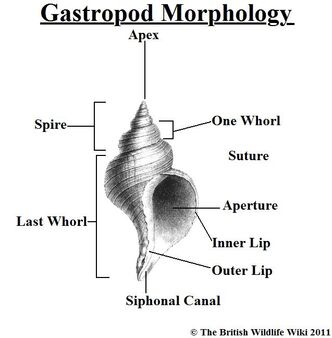
Gastropods are characterized by having a true head, an unsegmented body, a broad, flat foot and the possession of a single, often coiled shell, although this is lost in some slug groups. When present, the shell is in one piece and spirally coiled. The uppermost part of the shell is formed from the larval shell (the protoconch). The shell is partly or entirely lost in the juveniles or adults of some groups, with total loss occurring in several groups of land slugs and sea slugs. All fossil gastropods and most modern ones have a coiled shell, which is all that remains for the identification of fossil forms, while the identification of modern species is based largely on soft body parts [2]. The mantle cavity and visceral mass undergo torsion. Torsion takes place during the veliger stage, usually very rapidly. Veligers are at first bilaterally symmetric, but torsion destroys this pattern and results in an asymmetric adult. Some species reverse torsion ("detorsion"), but evidence of having passed through a twisted phase can be seen in the anatomy of these forms [6]. Torsion in gastropods has the unfortunate result of waste being expelled from the gut and nephridia near the gills. A variety of morphological and physiological adaptations have arisen to separate water used for respiration from water bearing waste products [6]. There is also usually a well-developed radula. They also have a muscular foot which is used for "creeping" locomotion in most species, while in some it is modified for swimming or burrowing. The foot is usually rather large and typically bears an operculum that seals the shell opening (aperture) when the head-foot is retracted into the shell. They move by producing a mucus lubricant under the flat ventral surface of the foot and a series of muscular contractions allow them to “slide” across the substrate. Most gastropods have a well-developed head that includes eyes (short to long stalks), 1-2 pairs of tentacles, and a concentration of nervous tissue (ganglion) [6]. The mantle edge in some taxa is extended anteriorly to form an inhalant siphon and this is sometimes associated with an elongation of the shell opening (aperture) [5]. The nervous and circulatory systems are well developed with the concentration of nerve ganglia being a common evolutionary theme. Many snails have an operculum, a horny plate that seals the opening when the snail's body is drawn into the shell. Externally, gastropods appear to be bilaterally symmetrical, however, they are one of the most successful clades of asymmetric organisms known [5].
 Variation in shell morphology in some marine gastropods.[3]
Variation in shell morphology in some marine gastropods.[3]
Ecological Importance
Because of their abundance and diversity, gastropoda play important roles in ecosystem functions by serving as prey for many other species and promoting the decomposition of dead plant/ vegetable matter and the subsequent recycling of nutrients [7]. They eat very low on the food web, as most land snails will consume rotting vegetation like moist leaf litter, and also fungi and sometimes eat soil directly. Indirectly, they are of great importance as furnishing food for many fish and other animals. Snails specifically can be of economic importance carrying parasites that affect both humans and animals.
References
- [1] Holthuis, B.V. (1995): Evolution between marine and freshwater habitats: a case study of the gastropod suborder Neritopsina. Ph.D. thesis, University of Washington
- [2] Allaby, M. 2020. A Dictionary of Zoology. Oxford University Press, Incorporated, Oxford, UNITED KINGDOM.
- [3] “The Gastropoda.” Ucmp.berkeley.edu, 1999, ucmp.berkeley.edu/taxa/inverts/mollusca/gastropoda.php.
- [4] “Gastropoda.” Wikipedia, 29 Nov. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gastropoda.
- [5] “Mollusca: Gastropoda.” Ucmp.berkeley.edu, ucmp.berkeley.edu/mollusca/mollusca/gastropoda/gastropoda.html.
- [6] Myers, P., and J. B. Burch. 2001. Gastropoda. https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Gastropoda/.
- [7] P. Bloch, C. 2012. Why Snails? How Gastropods Improve Our Understanding of Ecological Disturbance. Bridgewater Review Vol. 31.