Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a group of phytonutrients found in all plants on the planet. Functions of these chemicals in plants include UV protection, defense against invasive pathogens, pigmentation, and signaling in symbiosis. This group of chemicals can be broken down further into subgroups based on the makeup of their chemical structures. In foods, flavonoids are full of natural antioxidants and can be found in a multitude of food types.
Chemical structures
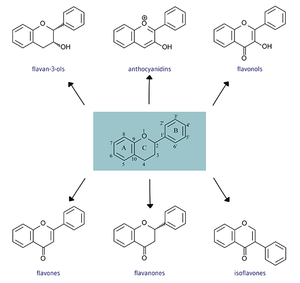
All flavonoids consist of phenolic and pyrane rings and are generally insoluble. [2] Flavonoids differ in the arrangement of hydroxyl, methoxy, and glycosidic groups and from there form subgroups that include more specific chemicals. [4]
Flavones -Apigenin, Luteolin
Flavanones -Hesperetin, Naringenin, Eriodictyol
Flavonols -Quercetin, Kaempferol, Myricetin, Isorhamnetin
Flavan-3-ols -Catechins, Epicatechins, Epicatechin3-gallate, Epigallocatechin, Epigallocatechin 3-gallate, Gallocatechin, Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-3’-digallate, Theaflavin 3’-gallate, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Thearubigins
Anthocyanidins -Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Petunidin
=
Role in plant growth
Presence in foods

Flavonoids have been discovered to play a big role in the presence of antioxidants in common food sources. Antioxidants, often sought after for their propensity to encourage tbc...
Medicinal applications
References
[4] Bhagwat, S., Haytowitz, D.B. Holden, J.M. (Ret.). 2014. USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods, Release 3.1. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Nutrient Data Laboratory Home Page: http://www.ars.usda.gov/nutrientdata/flav
[5] Kyle, J.A.M. et al. Flavonoids, chemistry, biochemistry and applications. In Flavonoids in Foods. Anderson, O.M. et al., Ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl. 2006