Ectomycorrhizal Fungi
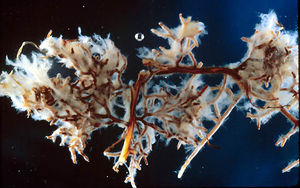
Ectomycorrhizal (ECM) fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots. Only about 2% of the plant species on earth form endomycorrhizal relationships, but therein exist some of the most environmentally and economically important species. [1]
Structures
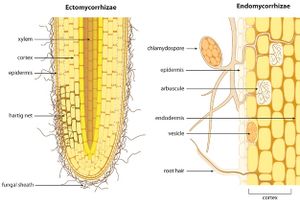
Mantle
A layer encasing the outside of the root tip in either a loose gathering or tight alignment of hyphae. The presence of the mantle can sometimes hinder root hair growth if the root is secured tightly.
Hartig net
A network of hyphae strands that work around root cells, as they make their way through the cortex towards the middle of the root.
Extraradical hyphae
Fruiting bodies
References
[1] Tedersoo, Leho; May, Tom W.; Smith, Matthew E. (2010). "Ectomycorrhizal lifestyle in fungi: global diversity, distribution, and evolution of phylogenetic lineages" (PDF). Mycorrhiza. 20 (4): 217–263. doi:10.1007/s00572-009-0274-x. PMID 20191371.
[2] Dighton, J. "Mycorrhizae." Encyclopedia of Microbiology (2009): 153-162.