Microarthropods: Difference between revisions
Created page with "=Overview= Link title Soil microarthropods include chelicerates (mites, spiders, and pseudoscorpions), myriapods (centipedes, millipedes, and symphylans), crustaceans (sm..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Overview= | =Overview= | ||
[[ | [[File:1_microarthropods_scaled.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Food Chain]] | ||
Soil microarthropods include chelicerates (mites, spiders, and pseudoscorpions), myriapods (centipedes, millipedes, and symphylans), crustaceans (small aquatic forms often found in water features), springtails, and insects. Many groups do not have popular names; proturans and diplurans, for instance, are small soil arthropods related to insects. | Soil microarthropods include chelicerates (mites, spiders, and pseudoscorpions), myriapods (centipedes, millipedes, and symphylans), crustaceans (small aquatic forms often found in water features), springtails, and insects. Many groups do not have popular names; proturans and diplurans, for instance, are small soil arthropods related to insects. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
Microarthropods are too small and numerous to be sampled as individuals so small pieces of habitat are collected and the microarthropods are then extracted from them in a laboratory. Most of the methods used for microarthropod extraction are either variations of the Tullgren funnel, floatation in solvents, or filtration. | Microarthropods are too small and numerous to be sampled as individuals so small pieces of habitat are collected and the microarthropods are then extracted from them in a laboratory. Most of the methods used for microarthropod extraction are either variations of the Tullgren funnel, floatation in solvents, or filtration. | ||
[[File:tullgren.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Tullgren Funnel]] | |||
=Biodiversity= | =Biodiversity= | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
Soil arthropods are significant reservoirs of biodiversity. In an extensive review, reports show that at most 10% of soil microarthropod populations have been explored and 10% of species described. | Soil arthropods are significant reservoirs of biodiversity. In an extensive review, reports show that at most 10% of soil microarthropod populations have been explored and 10% of species described. | ||
[[File:457065_1_En_26_Fig5_HTML.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Microarthropod Biodiversity]] | |||
=Role in Soil Ecology= | =Role in Soil Ecology= | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 5 May 2019
Overview

Soil microarthropods include chelicerates (mites, spiders, and pseudoscorpions), myriapods (centipedes, millipedes, and symphylans), crustaceans (small aquatic forms often found in water features), springtails, and insects. Many groups do not have popular names; proturans and diplurans, for instance, are small soil arthropods related to insects.
Much of the microarthropod group are discovered in most types of soils. A square meter of woodland floor could contain hundreds of thousands of individuals representing thousands of different species, mainly mites and collembola. Microarthropods have a substantial impact on the decomposition process in the forest floor and are important reservoirs of biodiversity in forest ecosystems
Microarthropods form an important set of connections in food chains/webs. They feed on fungi and nematodes and are prey for macroarthropods such as spiders, beetles, ants, and centipedes.
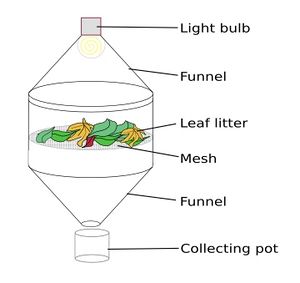
Extraction Methods
Microarthropods are too small and numerous to be sampled as individuals so small pieces of habitat are collected and the microarthropods are then extracted from them in a laboratory. Most of the methods used for microarthropod extraction are either variations of the Tullgren funnel, floatation in solvents, or filtration.
Biodiversity
Soils, including the deepest horizons and the rhizosphere, constitute a huge reservoir of understudied biodiversity, yet our sampling techniques may be inadequate to assess the diversity and abundance of soil fauna.
Temperate forest floors with large accumulation of organic matter support high numbers of microarthropods compared to tropical forests where the organic layer is thin.
Mites outnumber collembolans but these become more abundant in some situations. Among the mites themselves, the oribatids usually dominate but the Prostigmata may develop large populations in cultivated soils with a surface crust of algae. After cultivation asigmatic mites have been seen to increase dramatically.
Soil arthropods are significant reservoirs of biodiversity. In an extensive review, reports show that at most 10% of soil microarthropod populations have been explored and 10% of species described.

Role in Soil Ecology
While soil fauna is generally acknowledged as being important for soil aggregation, direct empirical evidence is scarce for microarthropods, including mites and collembolans, the two most abundant and diverse groups. This is surprising given that these animals can occur at high densities, and given their role in the processing of organic matter via chemical, physical and biological mechanisms
Due to their relatively small body size and total biomass, which is lower than that of fungi, bacteria and other taxa such as nematodes and protozoa, microarthropods may rather indirectly than directly affect soil structure. However, in some cases the impact of the production of assumedly large amounts of organic material in form of eggs might play an important role as direct starting points for microaggregate formation.