Animals: Difference between revisions
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Characteristics == | == Characteristics == | ||
[[File:Blastula.jpg]] | [[File:Blastula.jpg|200px|thumb|left|The outer cells of a blastula are the blastomeres, they surround a fluid filled cavity surrounding the blastocoele. This is an embryo of an animal cell in its early stages.]] | ||
Animals are multi-cellular organisms and, with the certain exceptions, these cells form specialized groups called tissues. These tissues have many different functions including, locomotion, structure, digestion, and various other processes necessary for life. These tissues begin to be created when the blastula is formed. The blastula is a hollow sphere of zygotic cells that forms after repeated division of fertilized animal egg. This hollow sphere begins the formation of the internal organs and tissues. A non-insignificant portion of tissues is not comprised of cells, they have a large amount of extracellular space in them. This space is mostly filled by the extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix is comprised of macromolecules such as proteins and polysaccharides. These molecules are produced by the cells in the tissues and they also arrange them within the tissues. The extracellular matrix is more prevalent in connective tissue and can calcify to form bones and similar structures. | Animals are multi-cellular organisms and, with the certain exceptions, these cells form specialized groups called tissues. These tissues have many different functions including, locomotion, structure, digestion, and various other processes necessary for life. These tissues begin to be created when the blastula is formed. The blastula is a hollow sphere of zygotic cells that forms after repeated division of fertilized animal egg. This hollow sphere begins the formation of the internal organs and tissues. A non-insignificant portion of tissues is not comprised of cells, they have a large amount of extracellular space in them. This space is mostly filled by the extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix is comprised of macromolecules such as proteins and polysaccharides. These molecules are produced by the cells in the tissues and they also arrange them within the tissues. The extracellular matrix is more prevalent in connective tissue and can calcify to form bones and similar structures. | ||
Animals are heterotrophic, they can not produce their own nutrients for aerobic respiration. Like fungi, animals must consume complex carbon molecules for aerobic respiration. These complex nutrients can be acquired by the from other organisms, live or dead. Detritovores consume the tissues of dead organisms. Grazers consume parts of still living organisms, for the most part these organisms are herbivores consuming mostly plant matter. Predators kill and consume other organisms mainly animals. Parasites and parasitoids both grow and develop either within or on other organisms, taking nutrients from them. Parasitoids, however kill their hosts. | Animals are heterotrophic, they can not produce their own nutrients for aerobic respiration. Like fungi, animals must consume complex carbon molecules for aerobic respiration. These complex nutrients can be acquired by the from other organisms, live or dead. Detritovores consume the tissues of dead organisms. Grazers consume parts of still living organisms, for the most part these organisms are herbivores consuming mostly plant matter. Predators kill and consume other organisms mainly animals. Parasites and parasitoids both grow and develop either within or on other organisms, taking nutrients from them. Parasitoids, however kill their hosts. | ||
[[File:Animal Cell]] | [[File:Animal Cell.jpeg|200px|thumb|right|An animal cell with the organelles labeled. Notice the lack of a cell wall in the animal cell]] | ||
The cells of animals are eukaryotic, meaning they surrounded by a cell membrane and have a nucleus with all of the genetic data of the cell inside. The biggest difference between animal cells and the cells of plants and fungi is that animal cells lack a cell wall. This lack of a cell wall allows for the differentiation of cells and the production of tissues. Most animal cells are diploid, therefore chromosomes exist in homologous pairs.These pairs break up during mitosis, and during meiosis these cells cross-over and ten divide to form haploid cells. The organelles within an animal cell are mostly made up of membranes, or in the case of mitochondria the remnants of a symbiotic bacteria. Certain organelles are found more often in animal cells, such as the centrioles which aid in the process of cell division. | The cells of animals are eukaryotic, meaning they surrounded by a cell membrane and have a nucleus with all of the genetic data of the cell inside. The biggest difference between animal cells and the cells of plants and fungi is that animal cells lack a cell wall. This lack of a cell wall allows for the differentiation of cells and the production of tissues. Most animal cells are diploid, therefore chromosomes exist in homologous pairs.These pairs break up during mitosis, and during meiosis these cells cross-over and ten divide to form haploid cells. The organelles within an animal cell are mostly made up of membranes, or in the case of mitochondria the remnants of a symbiotic bacteria. Certain organelles are found more often in animal cells, such as the centrioles which aid in the process of cell division. | ||
Revision as of 20:35, 6 March 2018
Members of the biological kingdom of Animalia are animals. Animals are eukaryotic organisms that are generally multi-cellular,oxygen dependent, heterotrophic, motile, and sexually reproductive. The cells of an animal do not have a rigid cell wall and, like other eukaryotic organisms, has organelles from folded membranes. Animal zygotes form a blastula during the development of an embryo to aid in the development of organs and other body structures. There are millions of estimated species of animals in the world and most of them are predicted to be insects. Animals are a major part of most of the ecosystems on the planet forming the majority of the food-webs in these ecosystems. Many species of animals spend at least a portion of their lives in soil.
Characteristics
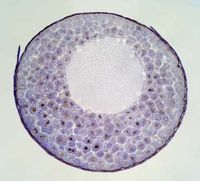
Animals are multi-cellular organisms and, with the certain exceptions, these cells form specialized groups called tissues. These tissues have many different functions including, locomotion, structure, digestion, and various other processes necessary for life. These tissues begin to be created when the blastula is formed. The blastula is a hollow sphere of zygotic cells that forms after repeated division of fertilized animal egg. This hollow sphere begins the formation of the internal organs and tissues. A non-insignificant portion of tissues is not comprised of cells, they have a large amount of extracellular space in them. This space is mostly filled by the extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix is comprised of macromolecules such as proteins and polysaccharides. These molecules are produced by the cells in the tissues and they also arrange them within the tissues. The extracellular matrix is more prevalent in connective tissue and can calcify to form bones and similar structures.
Animals are heterotrophic, they can not produce their own nutrients for aerobic respiration. Like fungi, animals must consume complex carbon molecules for aerobic respiration. These complex nutrients can be acquired by the from other organisms, live or dead. Detritovores consume the tissues of dead organisms. Grazers consume parts of still living organisms, for the most part these organisms are herbivores consuming mostly plant matter. Predators kill and consume other organisms mainly animals. Parasites and parasitoids both grow and develop either within or on other organisms, taking nutrients from them. Parasitoids, however kill their hosts.
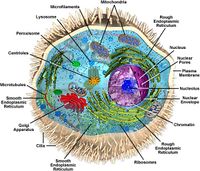
The cells of animals are eukaryotic, meaning they surrounded by a cell membrane and have a nucleus with all of the genetic data of the cell inside. The biggest difference between animal cells and the cells of plants and fungi is that animal cells lack a cell wall. This lack of a cell wall allows for the differentiation of cells and the production of tissues. Most animal cells are diploid, therefore chromosomes exist in homologous pairs.These pairs break up during mitosis, and during meiosis these cells cross-over and ten divide to form haploid cells. The organelles within an animal cell are mostly made up of membranes, or in the case of mitochondria the remnants of a symbiotic bacteria. Certain organelles are found more often in animal cells, such as the centrioles which aid in the process of cell division.
Taxonomy and Diversity
There are roughly 1.7 million described species in the animal kingdom. These animals are spread across 40 different phyla. Arthropods comprise roughly 1.3 million of these species and are by far the most numerous among them representing about 80% of the kingdom. The next largest phylum are the mollusks representing about 120 thousand species and having less than 10% of the diversity of the arthropods. The phylum Craniata includes all vertebrates representing 85 thousand species. 35 thousand of these species are fish, 16 thousand are mammals, 15 thousand are reptiles, 11 thousand are birds, and 7 thousand are amphibians.