Amoozemeter: Difference between revisions
Created page with " == Description == right|350px| Fig 1. 'Amoozemeter' [1] |thumb left|300px| Fig 2. Dr. Aziz Amoozegar ''Professor of Soil Physics at North Carolina State University'' [2]| thumb The Amoozemeter, also known as a compact constant head permeameter (CCH), was developed in 1999 by Dr. Aziz Amoozegar, a professor of Soil Physics at North Carolina State University[1][2]. The Amoozemeter is described as an experimental t..." |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
[[File:Amooze.jpg|right|350px| Fig 1. 'Amoozemeter' | [[File:Amooze.jpg|right|350px| Fig 1. 'Amoozemeter' | ||
<ref name= "Amoozemeter"> Jo House. 2019.Amoozemeter Field Demonstration for Determining Landfill Clay Liner Hydraulic Conductivity. Civil & Environmental Consultants Inc</ref> | |||
|thumb]] | |thumb]] | ||
[[File:Faculty_AzizAmoozegar-1.jpg|left|300px| Fig 2. Dr. Aziz Amoozegar ''Professor of Soil Physics at North Carolina State University'' [ | [[File:Faculty_AzizAmoozegar-1.jpg|left|300px| Fig 2. Dr. Aziz Amoozegar ''Professor of Soil Physics at North Carolina State University'' <ref name="Aziz Amoozegar" Aziz Amoozegar. NC State University (Department of Crops and Soil Sciences). https://cals.ncsu.edu/crop-and-soil-sciences/people/sscaag/.<ref name="Jo House" Jo House. 2019. Amoozemeter Field Demonstration for Determining Landfill [[Clay]] Liner Hydraulic Conductivity. Civil & Environmental Consultants. Inc.</ref> | ||
thumb | thumb | ||
The Amoozemeter, also known as a compact constant head permeameter (CCH), was developed in 1999 by Dr. Aziz Amoozegar, a professor of [[Soil]] Physics at North Carolina State University | The Amoozemeter, also known as a compact constant head permeameter (CCH), was developed in 1999 by Dr. Aziz Amoozegar, a professor of [[Soil]] Physics at North Carolina State University. | ||
The Amoozemeter is described as an experimental tool vital in the process of measuring saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) within the porespace of the unsaturated zone.[ | The Amoozemeter is described as an experimental tool vital in the process of measuring saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) within the porespace of the unsaturated zone. <ref name= "Parker Price"> Price, K., C. R. Jackson, and A. J. Parker. 2010. Variation of surficial soil hydraulic [[properties]] across land uses in the southern Blue Ridge Mountains, North Carolina, USA. Journal of Hydrology 383:256–268 </ref> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
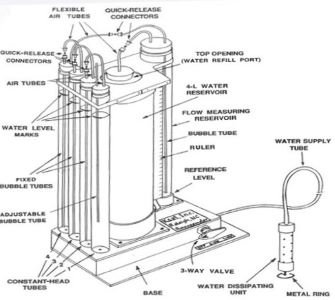
Standard procedures for determining the level of saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) within the unsaturated zone are often difficult to perform. Saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) can be determined by the constant-head well permeameter technique or the Amoozemeter in less than 30 minutes, using a few liters of water and small-diameter auger holes. The Amoozemeter or compact constant-head (CCH) permeameter is designed to maintain a constant height of water (>5 cm) at the bottom of a 4 to 10 cm diameter hole in the unsaturated zone, and measure the amount of water flowing into the hole. The main unit of the Amoozemeter is used for measuring Ks from the soil surface to a depth of 2 m. To determine saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) beyond a 2-m depth, a special flow-measuring reservoir, equipped with a portable pressure transducer, is connected to the device and inserted to the bottom of the hole. The Amoozemeter is designed with a water capacity of 5 liters, capable of delivering a maximum flow rate of 3 × 10−6 m3s, can handle most landscapes without additional aid, and is easily transported. | Standard procedures for determining the level of saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) within the unsaturated zone are often difficult to perform. Saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) can be determined by the constant-head well permeameter technique or the Amoozemeter in less than 30 minutes, using a few liters of water and small-diameter auger holes. The Amoozemeter or compact constant-head (CCH) permeameter is designed to maintain a constant height of water (>5 cm) at the bottom of a 4 to 10 cm diameter hole in the unsaturated zone, and measure the amount of water flowing into the hole. The main unit of the Amoozemeter is used for measuring Ks from the soil surface to a depth of 2 m. <ref name="Methods for Measuring Hydraulic Conductivity and Drainable [[Porosity]]" Methods for Measuring Hydraulic Conductivity and Drainable Porosity. Agricultural Drainage /, American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America, 1999, https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr38</ref> To determine saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) beyond a 2-m depth, a special flow-measuring reservoir, equipped with a portable pressure transducer, is connected to the device and inserted to the bottom of the hole. The Amoozemeter is designed with a water capacity of 5 liters, capable of delivering a maximum flow rate of 3 × 10−6 m3s, can handle most landscapes without additional aid, and is easily transported <ref name="Amoozegar" Amoozegar, A. 2020. Examination of models for determining saturated hydraulic conductivity by the constant head well permeameter method. Soil and Tillage Research 200:104572.</ref> | ||
. | |||
==Video Tutorial== | ==Video Tutorial== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 21: | ||
|thumb]] | |thumb]] | ||
How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat. 2011.[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1pkBUl9sdOc] | How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat. 2011. [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1pkBUl9sdOc] <ref name= "How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat" How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat. 2011. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1pkBUl9sdOc</ref> | ||
== | == References == | ||
<refernces/> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:53, 9 May 2025
Description

[[File:Faculty_AzizAmoozegar-1.jpg|left|300px| Fig 2. Dr. Aziz Amoozegar Professor of Soil Physics at North Carolina State University Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag
Function
Standard procedures for determining the level of saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) within the unsaturated zone are often difficult to perform. Saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ksat) can be determined by the constant-head well permeameter technique or the Amoozemeter in less than 30 minutes, using a few liters of water and small-diameter auger holes. The Amoozemeter or compact constant-head (CCH) permeameter is designed to maintain a constant height of water (>5 cm) at the bottom of a 4 to 10 cm diameter hole in the unsaturated zone, and measure the amount of water flowing into the hole. The main unit of the Amoozemeter is used for measuring Ks from the soil surface to a depth of 2 m. Cite error: Invalid parameter in <ref> tag
.
Video Tutorial
How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat. 2011. [1] <ref name= "How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat" How to Use an Amoozemeter for Soil Ksat. 2011. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1pkBUl9sdOc</ref>
References
<refernces/>
- ↑ Jo House. 2019.Amoozemeter Field Demonstration for Determining Landfill Clay Liner Hydraulic Conductivity. Civil & Environmental Consultants Inc