Hammerhead Worm: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
''Bipalium'', also known as the hammerhead worm, land planarian, or shovel-head garden worm, is a genus of invasive flatworm found in moist terrestrial environments in the northeastern United States [2]. The hammerhead worm is native to | ''Bipalium'', also known as the hammerhead worm, land planarian, or shovel-head garden worm, is a genus of invasive flatworm found in moist terrestrial environments in the northeastern United States [2]. The hammerhead worm is native to Southeast Asia and was introduced in 1891 [1]. This is easily identifiable by its distinct flattened body and crescent-shaped head. The worms are most often yellow, orange, or light brown, with a varying number of darker brown stripes running the length of the body [2]. Hammerhead worms pose a threat to natural ecosystems, as there are at least three species that have been found to feed exclusively on earthworms. They also pose a potential threat to agricultural operations, especially those operating in warm, moist environments [3]. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
=== Habitat and Range === | === Habitat and Range === | ||
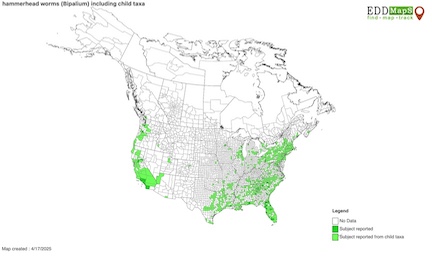
Hammerhead [[flatworms]] thrive in moist environments, including forests and agricultural fields. They are found amongst the upper [[soil]] layers and in leaf litter [2]. Although these worms prefer warm, wet environments, they are highly adaptive to different environments, including temperate forests in midlatitudes. This element allows hammerhead worms to invade higher latitudes than | Hammerhead [[flatworms]] thrive in moist environments, including forests and agricultural fields. They are found amongst the upper [[soil]] layers and in leaf litter [2]. Although these worms prefer warm, wet environments, they are highly adaptive to different environments, including temperate forests in midlatitudes. This element allows hammerhead worms to invade higher latitudes than those to which they are native. In their native range of Southeast Asia, hammerhead flatworms live in soils. | ||
Revision as of 16:32, 17 April 2025

| |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
|---|---|
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Turbellaria |
| Order: | Tricladida |
| Family: | Geoplanidae |
| Genus: | Bipalium |
| Source: County of Brant [4] | |
Description
Bipalium, also known as the hammerhead worm, land planarian, or shovel-head garden worm, is a genus of invasive flatworm found in moist terrestrial environments in the northeastern United States [2]. The hammerhead worm is native to Southeast Asia and was introduced in 1891 [1]. This is easily identifiable by its distinct flattened body and crescent-shaped head. The worms are most often yellow, orange, or light brown, with a varying number of darker brown stripes running the length of the body [2]. Hammerhead worms pose a threat to natural ecosystems, as there are at least three species that have been found to feed exclusively on earthworms. They also pose a potential threat to agricultural operations, especially those operating in warm, moist environments [3].

Behaviors
Habitat and Range
Hammerhead flatworms thrive in moist environments, including forests and agricultural fields. They are found amongst the upper soil layers and in leaf litter [2]. Although these worms prefer warm, wet environments, they are highly adaptive to different environments, including temperate forests in midlatitudes. This element allows hammerhead worms to invade higher latitudes than those to which they are native. In their native range of Southeast Asia, hammerhead flatworms live in soils.
Life Cycle
Impact as an Invasive Species
Bipalium has the ability to reproduce through binary fission. This means that a single worm can spontaneously split into two, and each half will regrow the missing half in approximately a week.
References
[6] EDDMapS. 2025. Early Detection & Distribution Mapping System. The University of Georgia - Center for Invasive Species and Ecosystem Health. Available online at http://www.eddmaps.org/; last accessed April 17, 2025.