Moss: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:File.jpeg|200px|thumb|left|Sphagnum moss]] | |||
{{Taxonomy | {{Taxonomy | ||
| common_name = moss | | common_name = moss | ||
| Line 6: | Line 10: | ||
==Physical Characteristics== | ==Physical Characteristics== | ||
[[File:mossstructure.png|left|Basic moss structure.|thumb|150px|]] | |||
===Structure=== | |||
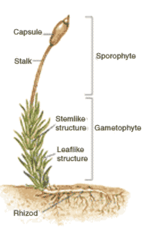
Mosses (Bryophyta) are non-vascular plants in the broader parent group Bryophyta, which includes Liverworts and Hornworts (Raven et al. 2013). They are the most specious of the three divisions of bryophytes, with over 12,000 species worldwide (Crandall-Stotler and Bartholomew-Began 2007). Mosses are herbaceous photosynthetic plants that absorb water and nutrients through their leaf-like structures. They are non-vascular, as they lack lignified water- and nutrient-conducting tissue called xylem and phloem (Ligrone et al. 2000). Additionally, mosses lack true roots, instead, they have multicellular thread-like structures called rhizoids that anchor the plant to the substrate (Raven et al. 2013). Like other bryophytes, mosses are dominated by their haploid, gametophytic generation and reproduce using spores. | |||
===Life Cycle=== | |||
[[File:Moss_3.png|Moss Life Cycle.|thumb|right|300px]] | |||
: Like vascular plants, mosses exhibit alternating heteromorphic generations. The gametophyte generation is typically larger and independent, while the sporophyte generation is smaller and nutritionally dependent on the parent gametophyte(Cove et al. 2006). The life cycle begins when haploid spores are released from the capsule of the mature sporophyte and germinate into protonemata, and then later into male and female gametophytes. The gametophytes have either male (antheridia) or female (archegonia) reproductive organs (Reski 1998). Haploid sperm are released from the mature antheridia and swim in the water to the archegonia which house the non-motile egg. Fertilization occurs in the archegonium to produce a diploid zygote, which divides mitotically to form a young sporophyte. As the it matures, the archegonium enlarges to protect the sporophyte until maturation is reached. The mature sporophyte consists of the stalk and capsule (sporangium). Meiosis occurs within the sporangium, producing haploid spores which will be released to form the gametophytic generation (Raven et al. 2013). | |||
==Environmental Role== | ==Environmental Role== | ||
: Mosses play an vital role in stabilizing [[soil]], reducing erosion, and reducing the risks of flooding by absorbing excess water. Their rhizoids can hold on to [[clay]], gravel, and sandy soil substrates. Along with absorbing moisture, mosses are an important carbon sink and could potentially play an important role in combating climate change. Additionally, mosses can filter other pollutants like excess sediment and salt used on roadways. Within the local environment mosses also have the ability to create humid microhabitats. [2] In some boreal and arctic ecosystems mosses are the primary plant type and are responsible for establishing soil layers, providing nutrients and habitats for new seeds to germinate, and providing areas for microinvertebrates to thrive [5]. | :Mosses play an vital role in stabilizing [[soil]], reducing erosion, and reducing the risks of flooding by absorbing excess water. Their rhizoids can hold on to [[clay]], gravel, and sandy soil substrates. Along with absorbing moisture, mosses are an important carbon sink and could potentially play an important role in combating climate change. Additionally, mosses can filter other pollutants like excess sediment and salt used on roadways. Within the local environment mosses also have the ability to create humid microhabitats. [2] In some boreal and arctic ecosystems mosses are the primary plant type and are responsible for establishing soil layers, providing nutrients and habitats for new seeds to germinate, and providing areas for microinvertebrates to thrive [5]. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 03:40, 10 March 2023

| moss | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Phylum: | Bryophyta |
Physical Characteristics
Structure
Mosses (Bryophyta) are non-vascular plants in the broader parent group Bryophyta, which includes Liverworts and Hornworts (Raven et al. 2013). They are the most specious of the three divisions of bryophytes, with over 12,000 species worldwide (Crandall-Stotler and Bartholomew-Began 2007). Mosses are herbaceous photosynthetic plants that absorb water and nutrients through their leaf-like structures. They are non-vascular, as they lack lignified water- and nutrient-conducting tissue called xylem and phloem (Ligrone et al. 2000). Additionally, mosses lack true roots, instead, they have multicellular thread-like structures called rhizoids that anchor the plant to the substrate (Raven et al. 2013). Like other bryophytes, mosses are dominated by their haploid, gametophytic generation and reproduce using spores.
Life Cycle
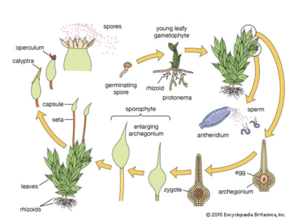
- Like vascular plants, mosses exhibit alternating heteromorphic generations. The gametophyte generation is typically larger and independent, while the sporophyte generation is smaller and nutritionally dependent on the parent gametophyte(Cove et al. 2006). The life cycle begins when haploid spores are released from the capsule of the mature sporophyte and germinate into protonemata, and then later into male and female gametophytes. The gametophytes have either male (antheridia) or female (archegonia) reproductive organs (Reski 1998). Haploid sperm are released from the mature antheridia and swim in the water to the archegonia which house the non-motile egg. Fertilization occurs in the archegonium to produce a diploid zygote, which divides mitotically to form a young sporophyte. As the it matures, the archegonium enlarges to protect the sporophyte until maturation is reached. The mature sporophyte consists of the stalk and capsule (sporangium). Meiosis occurs within the sporangium, producing haploid spores which will be released to form the gametophytic generation (Raven et al. 2013).
Environmental Role
- Mosses play an vital role in stabilizing soil, reducing erosion, and reducing the risks of flooding by absorbing excess water. Their rhizoids can hold on to clay, gravel, and sandy soil substrates. Along with absorbing moisture, mosses are an important carbon sink and could potentially play an important role in combating climate change. Additionally, mosses can filter other pollutants like excess sediment and salt used on roadways. Within the local environment mosses also have the ability to create humid microhabitats. [2] In some boreal and arctic ecosystems mosses are the primary plant type and are responsible for establishing soil layers, providing nutrients and habitats for new seeds to germinate, and providing areas for microinvertebrates to thrive [5].
References
- [1] Crandall-Stotler, B. J., and S. E. Bartholomew-Began. 2007. Morphology of Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta):3–13.
- [2] Crooks, V. 2021, February 22. Bryophytes. Text, Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute. https://stri.si.edu/story/bryophytes.
- [3] McHale, E. 2020, May 23. 7 interesting things about moss | Kew. https://www.kew.org/read-and-watch/moss.
- [4] Carter, J. S. 2010, September 12. Mosses and Ferns. https://biologyclermont.info/wwwroot/courses/lab2/mosses%20intro.htm.
- [5] Turetsky, M. R., B. Bond-Lamberty, E. Euskirchen, J. Talbot, S. Frolking, A. D. McGuire, and E.-S. Tuittila. 2012. The resilience and functional role of moss in boreal and arctic ecosystems. New Phytologist 196:49–67.