Wood frog: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Wood Frog otherwise known as ''Lithobates sylvaticus'' is a terrestrial frog found throughout North America [ | The Wood Frog otherwise known as ''Lithobates sylvaticus'' is a terrestrial frog found throughout North America [4]. In Greek '' Litho'' translates to "a stone", ''bates'' translates to "one that walks", and ''sylvaticus'' meaning "amidst the trees" [5]. They belong to the Order ''Anura'' and the Family ''Ranidae'' [2]. This species of frog is common and is not currently under any threat of extinction [4]. | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The Wood frog is a comparatively small frog. Fully grown adults are 1.5 to 3.25 inches in length [ | The Wood frog is a comparatively small frog. Fully grown adults are 1.5 to 3.25 inches in length [4]. Females are typically larger and more brightly colored than their male counterparts [4]. They can differ in color, but bodies typically range from a light tan to a dark brown [3]. Their most distinct feature is the coloration around their eyes. The Wood frog has two black markings that extend back from their eyes, resembling a mask [5]. The underbelly is white and sometimes has small grey marks [3]. This frog has two distinct ridges that run down their back. These ridges are known as Dorsolateral folds [5]. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[File:woodfrogmap.gif]] | [[File:woodfrogmap.gif]] | ||
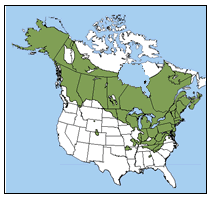
Wood frogs have a very large range. They are found in Canada and North America [ | Wood frogs have a very large range. They are found in Canada and North America [4]. Their range goes as far south as the Appalachian mountains and as far north as Alaska [5]. They can also be found in smaller populations in Alabama and Idaho [4]. The Wood frog is the only frog that lives in the Artic Circle, this is due to their ability to freeze [4]. | ||
Wood frogs typically like | Wood frogs typically like both deciduous and coniferous forests [5]. They gravitate towards forests with a closed canopy to keep out sunlight and keep in moisture [2]. This species likes lots of leaf litter and wood debris on the forest floor for shelter [3]. Especially in the winter, Wood frogs can go upland and seek refuge in the leaf litter while they hibernate [3]. When they are not breeding, they can be found in an moist forested areas, ravines, bogs or forested swamps. When spring comes they migrate into forested wetlands or other protected bodies of water to breed [2]. | ||
During mating season, these frogs find temporary pools of water of [[Vernal Pools|vernal pools]] [ | During mating season, these frogs find temporary pools of water of [[Vernal Pools|vernal pools]] [5]. These can be any cut off water sources like streams or ponds, and can even be in ditches. These are preferably free of fish to increase survivability of the offspring [5]. Wood frogs are diurnal and are rarely seen at night but often heard in loud choruses during mating season [4]. | ||
== Cold Tolerance == | == Cold Tolerance == | ||
Wood frogs | |||
Wood frogs are one of the only species of frog to live in the Artic Circle, this is due to their ability to freeze [4]. These frogs "freeze over" in the winter, this serves as hibernation [4]. The freezing process works by releasing large amounts of glucose into their bloodstream, this keeps their body cells from freezing, but not their other bodily fluids [3]. The distribution of liver glycogen enhances the survival of cells, tissues, and organs. This was seen by experimentally adding additional glucose to the Wood frog which increased its tolerance to freezing [1]. This glucose distribution raises the osmotic pressure of the body fluids, which in turn reduces the amount of ice that forms at any given temperature [1]. The Wood frog also creates and antifreeze using their urea [4]. These cryoprotectants keep the water within their cells from freezing because this would indeed kill them [4]. As winter ends the frogs will begin to thaw and begin the breeding process [4]. | |||
== Diet == | == Diet == | ||
Wood Frogs are omnivores. While inhabiting the forests as adults they feed on a variety of small invertebrates that they find on the forest floor. As tadpoles they will feed on algae or detritus and even larvae of amphibians. Cannibalism has often been observed in tadpoles when starvation is the alternative. | Wood Frogs are omnivores. While inhabiting the forests as adults they feed on a variety of small invertebrates that they find on the forest floor. As tadpoles they will feed on algae or detritus and even larvae of amphibians. Cannibalism has often been observed in tadpoles when starvation is the alternative. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
[1] | [1] Costanzo, Jon P., et al. “Cryoprotectants and Extreme Freeze Tolerance in a Subarctic Population of the Wood Frog.” PLOS ONE, vol. 10, no. 2, Feb. 2015, p. e0117234. PLoS Journals, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0117234. | ||
[2] | [2] Integrated Taxonomic Information System - Report. (n.d.). . https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=775197. | ||
[3] | [3] Wild things in your woods. (n.d.). . Cornell University. https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/blogs.cornell.edu/dist/a/7804/files/2018/05/Wood-Frog-23xt0xr-11v8dab.pdf. | ||
[4] Wood Frog. (n.d.). . Virginia Herpetological Society. https://www.virginiaherpetologicalsociety.com/amphibians/frogsandtoads/wood-frog/wood_frog.php. | [4] Wood frog. (n.d.). . National Wildlife Federation. https://www.nwf.org/educational-resources/wildlife-guide/amphibians/wood-frog#:~:text=Wood%20frogs%20are%20found%20in,lay%20eggs%20in%20vernal%20pools. | ||
[5] Wood Frog. (n.d.). . Virginia Herpetological Society. https://www.virginiaherpetologicalsociety.com/amphibians/frogsandtoads/wood-frog/wood_frog.php. | |||
Berven, Keith A., and Thaddeus A. Grudzien. “Dispersal in the Wood Frog (Rana Sylvatica): Implications for Genetic Population Structure.” Evolution, vol. 44, no. 8, 1990, pp. 2047–56. JSTOR, doi:10.2307/2409614. | Berven, Keith A., and Thaddeus A. Grudzien. “Dispersal in the Wood Frog (Rana Sylvatica): Implications for Genetic Population Structure.” Evolution, vol. 44, no. 8, 1990, pp. 2047–56. JSTOR, doi:10.2307/2409614. | ||
Conlon, J. M., et al. “Freeze Tolerance in the Wood Frog Rana Sylvatica Is Associated with Unusual Structural Features in Insulin but Not in Glucagon.” Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, vol. 21, no. 2, Oct. 1998, pp. 153–59. PubMed, doi:10.1677/jme.0.0210153. | Conlon, J. M., et al. “Freeze Tolerance in the Wood Frog Rana Sylvatica Is Associated with Unusual Structural Features in Insulin but Not in Glucagon.” Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, vol. 21, no. 2, Oct. 1998, pp. 153–59. PubMed, doi:10.1677/jme.0.0210153. | ||
“Explosive Breeding Reduces Egg and Tadpole Cannibalism in the Wood Frog, Rana Sylvatica.” Animal Behaviour, vol. 50, no. 3, Jan. 1995, pp. 731–39. www.sciencedirect.com, doi:10.1016/0003-3472(95)80133-2. | “Explosive Breeding Reduces Egg and Tadpole Cannibalism in the Wood Frog, Rana Sylvatica.” Animal Behaviour, vol. 50, no. 3, Jan. 1995, pp. 731–39. www.sciencedirect.com, doi:10.1016/0003-3472(95)80133-2. | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 14 March 2022
The Wood Frog otherwise known as Lithobates sylvaticus is a terrestrial frog found throughout North America [4]. In Greek Litho translates to "a stone", bates translates to "one that walks", and sylvaticus meaning "amidst the trees" [5]. They belong to the Order Anura and the Family Ranidae [2]. This species of frog is common and is not currently under any threat of extinction [4].
Description
The Wood frog is a comparatively small frog. Fully grown adults are 1.5 to 3.25 inches in length [4]. Females are typically larger and more brightly colored than their male counterparts [4]. They can differ in color, but bodies typically range from a light tan to a dark brown [3]. Their most distinct feature is the coloration around their eyes. The Wood frog has two black markings that extend back from their eyes, resembling a mask [5]. The underbelly is white and sometimes has small grey marks [3]. This frog has two distinct ridges that run down their back. These ridges are known as Dorsolateral folds [5].
Range and Habitat
Wood frogs have a very large range. They are found in Canada and North America [4]. Their range goes as far south as the Appalachian mountains and as far north as Alaska [5]. They can also be found in smaller populations in Alabama and Idaho [4]. The Wood frog is the only frog that lives in the Artic Circle, this is due to their ability to freeze [4].
Wood frogs typically like both deciduous and coniferous forests [5]. They gravitate towards forests with a closed canopy to keep out sunlight and keep in moisture [2]. This species likes lots of leaf litter and wood debris on the forest floor for shelter [3]. Especially in the winter, Wood frogs can go upland and seek refuge in the leaf litter while they hibernate [3]. When they are not breeding, they can be found in an moist forested areas, ravines, bogs or forested swamps. When spring comes they migrate into forested wetlands or other protected bodies of water to breed [2].
During mating season, these frogs find temporary pools of water of vernal pools [5]. These can be any cut off water sources like streams or ponds, and can even be in ditches. These are preferably free of fish to increase survivability of the offspring [5]. Wood frogs are diurnal and are rarely seen at night but often heard in loud choruses during mating season [4].
Cold Tolerance
Wood frogs are one of the only species of frog to live in the Artic Circle, this is due to their ability to freeze [4]. These frogs "freeze over" in the winter, this serves as hibernation [4]. The freezing process works by releasing large amounts of glucose into their bloodstream, this keeps their body cells from freezing, but not their other bodily fluids [3]. The distribution of liver glycogen enhances the survival of cells, tissues, and organs. This was seen by experimentally adding additional glucose to the Wood frog which increased its tolerance to freezing [1]. This glucose distribution raises the osmotic pressure of the body fluids, which in turn reduces the amount of ice that forms at any given temperature [1]. The Wood frog also creates and antifreeze using their urea [4]. These cryoprotectants keep the water within their cells from freezing because this would indeed kill them [4]. As winter ends the frogs will begin to thaw and begin the breeding process [4].
Diet
Wood Frogs are omnivores. While inhabiting the forests as adults they feed on a variety of small invertebrates that they find on the forest floor. As tadpoles they will feed on algae or detritus and even larvae of amphibians. Cannibalism has often been observed in tadpoles when starvation is the alternative.
Reproduction
The Wood frogs emerge from the leaf litter in late winter or early spring, usually March. The head to a nearby body of water and begin looking for a mate. The male wood frog has a short quack like mating call. Once the frogs pair the female will lay egg clutches of 300-1000 eggs. The eggs will hatch between 9 to 30 days after they are laid. Males will mature between 1 and 2 years and Females after about 3 years. Some individuals will only reproduce once in there lives, others two or three times as their life span is on average 4 years.
References
[1] Costanzo, Jon P., et al. “Cryoprotectants and Extreme Freeze Tolerance in a Subarctic Population of the Wood Frog.” PLOS ONE, vol. 10, no. 2, Feb. 2015, p. e0117234. PLoS Journals, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0117234.
[2] Integrated Taxonomic Information System - Report. (n.d.). . https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=775197.
[3] Wild things in your woods. (n.d.). . Cornell University. https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/blogs.cornell.edu/dist/a/7804/files/2018/05/Wood-Frog-23xt0xr-11v8dab.pdf.
[4] Wood frog. (n.d.). . National Wildlife Federation. https://www.nwf.org/educational-resources/wildlife-guide/amphibians/wood-frog#:~:text=Wood%20frogs%20are%20found%20in,lay%20eggs%20in%20vernal%20pools.
[5] Wood Frog. (n.d.). . Virginia Herpetological Society. https://www.virginiaherpetologicalsociety.com/amphibians/frogsandtoads/wood-frog/wood_frog.php.
Berven, Keith A., and Thaddeus A. Grudzien. “Dispersal in the Wood Frog (Rana Sylvatica): Implications for Genetic Population Structure.” Evolution, vol. 44, no. 8, 1990, pp. 2047–56. JSTOR, doi:10.2307/2409614.
Conlon, J. M., et al. “Freeze Tolerance in the Wood Frog Rana Sylvatica Is Associated with Unusual Structural Features in Insulin but Not in Glucagon.” Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, vol. 21, no. 2, Oct. 1998, pp. 153–59. PubMed, doi:10.1677/jme.0.0210153.
“Explosive Breeding Reduces Egg and Tadpole Cannibalism in the Wood Frog, Rana Sylvatica.” Animal Behaviour, vol. 50, no. 3, Jan. 1995, pp. 731–39. www.sciencedirect.com, doi:10.1016/0003-3472(95)80133-2.
Virginia Herpetological Society. http://www.virginiaherpetologicalsociety.com. Accessed 4 May 2021.
“Wood Frog | Vermont Center for Ecostudies.” Vermont Center for Ecostudies | Uniting People & Science for Conservation, 5 June 2014, https://vtecostudies.org/wildlife/amphibians/wood-frog/.