Flavonoids: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Flavonoids are a group of phytonutrients found in all plants on the planet. This group of chemicals can be broken down further into subgroups based on the makeup of their chemical structures. | Flavonoids are a group of phytonutrients found in all plants on the planet. Functions of these chemicals in plants include UV protection, defense against invasive pathogens, pigmentation, and signaling in symbiosis. This group of chemicals can be broken down further into subgroups based on the makeup of their chemical structures. In foods, flavonoids are full of natural antioxidants and can be found in a multitude of food types. | ||
==Chemical structures== | ==Chemical structures== | ||
[[File:Flav structures 2.0.png|thumb|Six subgroups of Flavonoids separated by chemical structure [1]]] | [[File:Flav structures 2.0.png|thumb|Six subgroups of Flavonoids separated by chemical structure [1]]] | ||
All flavonoids consist of phenolic and pyrane rings and are generally insoluble. | |||
==Role in plant root growth== | ==Role in plant root growth== | ||
== | ==Presence in foods== | ||
==Medicinal applications== | |||
Revision as of 21:38, 6 March 2018
Flavonoids are a group of phytonutrients found in all plants on the planet. Functions of these chemicals in plants include UV protection, defense against invasive pathogens, pigmentation, and signaling in symbiosis. This group of chemicals can be broken down further into subgroups based on the makeup of their chemical structures. In foods, flavonoids are full of natural antioxidants and can be found in a multitude of food types.
Chemical structures
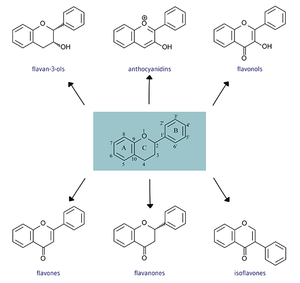
All flavonoids consist of phenolic and pyrane rings and are generally insoluble.