Plant roots: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
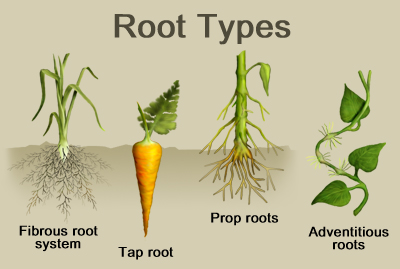
[[File:roottype.jpg]] | [[File:roottype.jpg]] | ||
== Citations == | |||
Gyssels, G., et al. “Impact of Plant Roots on the Resistance of Soils to Erosion by Water: a Review.” Progress in Physical Geography, vol. 29, no. 2, 2005, pp. 189–217., | |||
Revision as of 09:40, 18 April 2018
Overview
The root is typically the part of the plant that grows into the soil, helping to anchor the plant down. However, the plant root can be aerial in waterlogged soil, allowing the plant to breathe. The plant root also helps with the uptake of water and minerals.
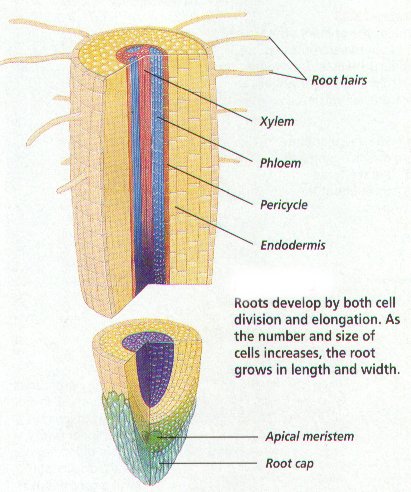
Parts of the plant root
The root hairs is a thin hairlike structure growing from the epidermal cell. These help with the absorption of moisture and nutrients from the soil. Xylem Phloem Pericycle Endodermis Apical meristem Root cap
Citations
Gyssels, G., et al. “Impact of Plant Roots on the Resistance of Soils to Erosion by Water: a Review.” Progress in Physical Geography, vol. 29, no. 2, 2005, pp. 189–217.,