Common Eastern Firefly (Photinus pyralis): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''Photinus pyralis'', also commonly referred to as the Common Eastern Firefly, Big Dipper Firefly, or Lightning Bug are a species of flying beetles. The Common Eastern Firefly is the most common firefly species in North America [1]. These beetles are known for the show they put on in late spring and early summer emitting a bioluminescence that is used to attract mates | ''Photinus pyralis'', also commonly referred to as the Common Eastern Firefly, Big Dipper Firefly, or Lightning Bug are a species of flying beetles. The Common Eastern Firefly is the most common firefly species in North America [1]. These beetles are known for the show they put on in late spring and early summer months by emitting a bioluminescence that is often used to attract mates [1]. | ||
[[File:CEFglowing_(1).jpg|thumb|300px|right|Common Eastern Firefly glowing]] | [[File:CEFglowing_(1).jpg|thumb|300px|right|Common Eastern Firefly glowing]] | ||
==Taxonomy== | ==Taxonomy== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
The average adult beetle is around 9 to 19 mm (0.4 to 0.7 inches) long [1] consisting of three main sections including the head, thorax and | The average adult beetle is around 9 to 19 mm (0.4 to 0.7 inches) long [1] consisting of three main sections including the head, thorax and abdomen. The shield like plate covering the beetles head has a black dot in the center surrounded by red and yellow with yellow on the outer most edge [2]. The wing covers are black and edged in yellow. Underneath the wing covers is pairs of wings and an abdomen that is black in color with respect to the last segment which is yellow. The last segment is the bioluminescent organ found to "glow". The beetles are have a hard exoskeleton with 6 jointed legs, two antennas, and compound eyes located on either side of the head [3] all of which are blackish brown in color. | ||
==Bioluminescence== | ==Bioluminescence== | ||
The creation of the bioluminescent light is formed with the presence of oxygen, magnesium, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) producing the complex organic compound luciferin. As luciferin oxidizes, a "cold light" is emitted [4]. The term "cold light" refers to majority of the energy produced is in the form of light with very little released as heat [1]. Each firefly species is found to have different lightning patterns. The male Common Eastern Firefly is found to have a single sustained yellow light while flying upwards forming the letter "J" [5]. The female fireflies are often found on long blades of grass emitting their own flashing signal to find a mate. While most of the bioluminescent is used to attract a mate, it may also be used to warn predators of their toxicity [6]. On some occasions the female Common Eastern Firefly is found luring in males by mimicking mating signals as bait [6]. | |||
==Habitat== | ==Habitat== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Ecosystem Importance== | ==Ecosystem Importance== | ||
The Common | The Common Eastern Firefly acts as both a predator and prey therefore contributing to food web stability [7]. The larva and adult fireflies can be found eating insects, snails, and earthworms [1]. While not many species feed off of the Common Eastern Firefly due to their toxicity, invertebrate predators such as spiders are found to be least affect by the toxins [7]. | ||
[[File:Fireflyproject-weebly-com_(1).png|300px|thumb|Life Cycle of Fireflies]] | [[File:Fireflyproject-weebly-com_(1).png|300px|thumb|Life Cycle of Fireflies]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
'''Eggs:''' Are about 1 mm in length and spherical in shape. They are found to hatch 4 weeks after being laid [1]. | '''Eggs:''' Are about 1 mm in length and spherical in shape. They are found to hatch 4 weeks after being laid [1]. | ||
'''Larva:''' The larvae live around 1 to 2 years. The larvae may be found eating [[insects]], snails, and earthworms [ | '''Larva:''' The larvae live around 1 to 2 years. The larvae may be found eating [[insects]], snails, and earthworms [8]. | ||
'''Pupa:''' Pupates are found within damp [[soil]] requiring 9 to 15 days to fully mature which is dependent on soil | '''Pupa:''' Pupates are found within damp [[soil]] requiring 9 to 15 days to fully mature which is dependent on soil temperature [9]. | ||
'''Adult:''' The adult fireflies live around 30 days with female fireflies laying up to 500 eggs in a season[1]. | '''Adult:''' The adult fireflies live around 30 days with female fireflies laying up to 500 eggs in a season [1]. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
[6] https://www.fllt.org/firefly-bioluminescence/#:~:text=The%20mostly%20nocturnal%20firefly%20larvae,bats%20that%20they%20are%20poisonous. | [6] https://www.fllt.org/firefly-bioluminescence/#:~:text=The%20mostly%20nocturnal%20firefly%20larvae,bats%20that%20they%20are%20poisonous. | ||
[7] https:// | [7] https://xerces.org/sites/default/files/publications/19-049_01_Firefly%20guidelines_web_1.pdf | ||
[8] https://www.lsuagcenter.com/profiles/bneely/articles/page1587050468972#:~:text=Larval%20Photinus%20can%20be%20found,to%20mature%20depending%20on%20temperature. | [8] https://www.lifeoncsgpond.com/common-eastern-firefly#:~:text=At%20dusk%2C%20a%20flying%2C%20flashing,with%20narrow%20yellow%20side%20margins. | ||
[9] https://www.lsuagcenter.com/profiles/bneely/articles/page1587050468972#:~:text=Larval%20Photinus%20can%20be%20found,to%20mature%20depending%20on%20temperature. | |||
Revision as of 12:44, 29 March 2025
Photinus pyralis, also commonly referred to as the Common Eastern Firefly, Big Dipper Firefly, or Lightning Bug are a species of flying beetles. The Common Eastern Firefly is the most common firefly species in North America [1]. These beetles are known for the show they put on in late spring and early summer months by emitting a bioluminescence that is often used to attract mates [1].

Taxonomy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Anthropoda
Class: Insecta
Order: Coleoptera
Family: Lampyridae
Genus: Photinus

Description
The average adult beetle is around 9 to 19 mm (0.4 to 0.7 inches) long [1] consisting of three main sections including the head, thorax and abdomen. The shield like plate covering the beetles head has a black dot in the center surrounded by red and yellow with yellow on the outer most edge [2]. The wing covers are black and edged in yellow. Underneath the wing covers is pairs of wings and an abdomen that is black in color with respect to the last segment which is yellow. The last segment is the bioluminescent organ found to "glow". The beetles are have a hard exoskeleton with 6 jointed legs, two antennas, and compound eyes located on either side of the head [3] all of which are blackish brown in color.
Bioluminescence
The creation of the bioluminescent light is formed with the presence of oxygen, magnesium, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) producing the complex organic compound luciferin. As luciferin oxidizes, a "cold light" is emitted [4]. The term "cold light" refers to majority of the energy produced is in the form of light with very little released as heat [1]. Each firefly species is found to have different lightning patterns. The male Common Eastern Firefly is found to have a single sustained yellow light while flying upwards forming the letter "J" [5]. The female fireflies are often found on long blades of grass emitting their own flashing signal to find a mate. While most of the bioluminescent is used to attract a mate, it may also be used to warn predators of their toxicity [6]. On some occasions the female Common Eastern Firefly is found luring in males by mimicking mating signals as bait [6].
Habitat
These beetles are nocturnal and crepuscular indicating they are most active at night and during dawn and dusk. The larvae can be found living on damp ground near streams. The adult beetles are typically found in meadows, wetlands, and edges of woodlands typically found in conditions of wet soils and tall grasses [3].
Ecosystem Importance
The Common Eastern Firefly acts as both a predator and prey therefore contributing to food web stability [7]. The larva and adult fireflies can be found eating insects, snails, and earthworms [1]. While not many species feed off of the Common Eastern Firefly due to their toxicity, invertebrate predators such as spiders are found to be least affect by the toxins [7].
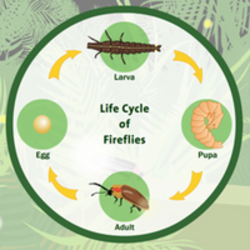
Life Cycle
The Common Eastern Firefly goes through the life cycle of metamorphous as the beetle transforms from larvae to adult. In the early stages it can be seen that both the eggs and larvae emit a soft glow to warn off predators [1].
Eggs: Are about 1 mm in length and spherical in shape. They are found to hatch 4 weeks after being laid [1].
Larva: The larvae live around 1 to 2 years. The larvae may be found eating insects, snails, and earthworms [8].
Pupa: Pupates are found within damp soil requiring 9 to 15 days to fully mature which is dependent on soil temperature [9].
Adult: The adult fireflies live around 30 days with female fireflies laying up to 500 eggs in a season [1].
References
[1] https://www.inaturalist.org/taxa/129350-Photinus-pyralis
[4]http://photobiology.info/Branchini2.html
[5] https://www.nps.gov/grsm/learn/nature/firefly-flash-patterns.htm
[7] https://xerces.org/sites/default/files/publications/19-049_01_Firefly%20guidelines_web_1.pdf