Prostigmata: Difference between revisions
m The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (<a rel="nofollow" class="external free" href="https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles">https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles</a>). |
m The LinkTitles extension automatically added links to existing pages (<a rel="nofollow" class="external free" href="https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles">https://github.com/bovender/LinkTitles</a>). |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
[1]Coleman, D. C., M. C. Callaham, and D. A. Crossley. 2018. FUNDAMENTALS OF SOIL ECOLOGY. 3Rd edition. Candice JancoCambridge, MA. | [1]Coleman, D. C., M. C. Callaham, and D. A. Crossley. 2018. FUNDAMENTALS OF [[Soil Ecology|SOIL ECOLOGY]]. 3Rd edition. Candice JancoCambridge, MA. | ||
[2]Contributors, W. 2012, July 18. Mite Life Cycle. https://en.wikivet.net/Mite_Life_Cycle. | [2]Contributors, W. 2012, July 18. Mite Life Cycle. https://en.wikivet.net/Mite_Life_Cycle. | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 29 April 2021
Definition
The Prostigmata (also known as "sucking mites") is a suborder of the Trombidiformes, found in the class Arachnida. These mites are one of the oldest suborders found on earth, together with the Oribatida, dating back to the Devonian Era. The prostigmatic mites contains a very diversified diet within its organisms, many are predators, but there are also families of fungal eating, plant eating, microbial eating and parasites. These mites can vary in size, from 0.1 reaching up to 10 millimeters.
Classification
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Chelicerata
Class: Arachnida
Subclass: Acari
Order: Trombidiformes
Suborder: Prostigmata
Examples of organisms and their diet:
1) Spider mites (Tetrachynus urticae), which eat plants, are known for being a pest.
2) Demodex mites are parasites to vertebrates, while invertebrates include Acarapis woodi that prey on honeybees.


3) Prostigmatic mites from the family Eupodidae are opportunistic organisms to fungi.
4) The families Eupodidae,Tarsonemidae, and Nanorchestidae feed on algae.
Characteristics
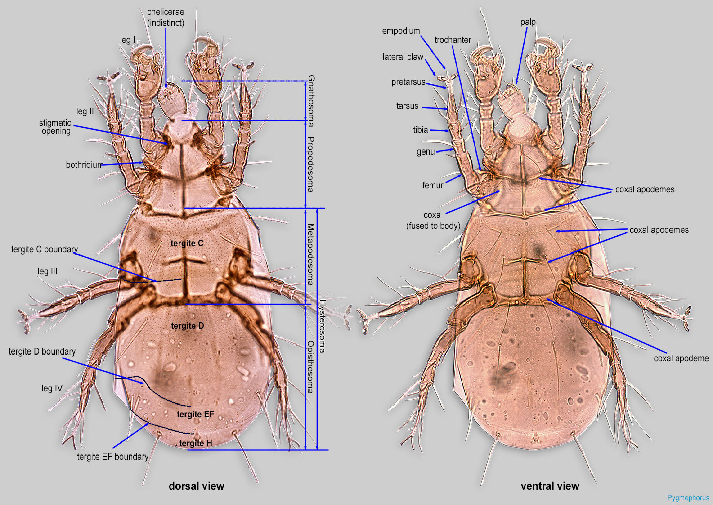
According to a study in the University of Michigan [5], these are the morphological features of the Prostigmata body:
1) Absence of the Tritosternum (Biflagellate structure in the ventral side of the body)
2) The leg joint is fused with their body
3) The stigmatic openings (used for feeding), are present but either near the chelicerae or on the dorsal side of the propodosoma
4) The empodial and lateral claws are usually present in some legs
5) The male Aedeagus (reproductive structure) can be both present or absent
6) The dispersal stage is not substantially different from the non-dispersal stage
7) The attachment organ is absent
8) The chelicerae is developed but sometimes indistinct
Detailed descriptions of each term can be found in their glossary page [6]
Prostigmata Life Cycle
Life cycle’s of arthropods are very similar between different organisms of different classes. While they have the same standard stages, the duration differs between species, with a total average of 3 weeks. Mites go through 5 stages before death: egg, larvae, protonymph, deuteronymph, adult.
1) Eggs: The eggs are laid on the host or on the soil by the female, the amount varies between species
2) Larva: The eggs hatch and larva emerge from them, which feeds on skin cells. In some species, this is the only parasitic stage, which can last 3 to 4 days
3) Nymph: The larvae goes through dormancy for 24 hours, and develop into a nymph, which has 2 stages. The whole stage has a 3 to 4 day period
4)Adult: After the nymphs develop into an adult, they can live either on the surface or by making burrows

References
[1]Coleman, D. C., M. C. Callaham, and D. A. Crossley. 2018. FUNDAMENTALS OF SOIL ECOLOGY. 3Rd edition. Candice JancoCambridge, MA.
[2]Contributors, W. 2012, July 18. Mite Life Cycle. https://en.wikivet.net/Mite_Life_Cycle.
[3]Contributors, W. 2021, April. Mite. Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mite#Reproduction_and_life_cycle.
[4]Contributors, W. 2021, March 15. Prostigmata. Wikimedia Foundation. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prostigmata.
[5]Klimov, P., B. OConnor, R. Ochoa, G. Bauchan, A. Redford, and J. Scher. 2016, October. Bee Mite ID. http://idtools.org/id/mites/beemites/bmites_morphology.php.
[6]Klimov, P., B. OConnor, R. Ochoa, G. Bauchan, A. Redford, and J. Scher. 2016, October. Bee Mite ID. http://idtools.org/id/mites/beemites/glossary.php#a.
[7]Murray, A. (n.d.). All about prostigmatid mites. https://www.chaosofdelight.org/all-about-mites-prostigmata.
[8]Proctor, H. 1998, August 12. Page: Tree of Life Trombidiformes. Trombidiform mites. http://tolweb.org/Trombidiformes/2568.