Testate amoebae: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===Definition=== | ===Definition=== | ||
'''Testate amoebae''' (Testacea, or Hyalosphenia) are amoeboid protists, differing from [[naked amoebae]] in that they inhabit a test, or shell. The '''test''' of the testate can be created entirely by the amoeba, in which it would create an organic, siliceous, or calcareous shell depending on the species of testate amoeba. These tests created entirely by the amoeba are known as '''autogenic tests'''. An '''xenogenic test''' is made up of particles of sediment collected by the amoeba which are then agglutinated together by secretions | '''Testate amoebae''' (Testacea, or Hyalosphenia) are amoeboid protists, differing from [[naked amoebae]] in that they inhabit a test, or shell. The '''test''' of the testate can be created entirely by the amoeba, in which it would create an organic, siliceous, or calcareous shell depending on the species of testate amoeba. These tests created entirely by the amoeba are known as '''autogenic tests''', as seen in figure 1. An '''xenogenic test''' is made up of particles of sediment collected by the amoeba which are then agglutinated together by secretions within the cell, as seen in figure 2. | ||
[[File: Arcella_discoides.jpg|thumb|300x300px|Figure 1: the ''autogenic'' test of Arcella discoides, made up of organic plates..]] | |||
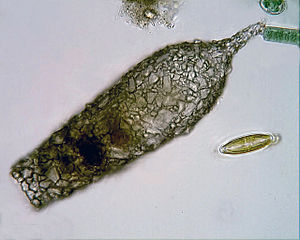
[[File:Difflugia_acuminata.jpg|thumb|300x300px|Figure 2: An ''xenogenic test'' of a Difflugia acuminata. Depicts an agglutinated test made up of mineral particles glued together with secretions from within the cell.]] | |||
===Habitat=== | ===Habitat=== | ||
This group of free-living microorganisms inhabit aquatic to moist habitats including: estuaries, lakes, rivers, wetlands, soils, litter, and moss habitats. They are able to live in both fresh and marine water, however, compared to naked amoeba, testate amoebae are less abundant in most soils. | This group of free-living microorganisms inhabit aquatic to moist habitats including: estuaries, lakes, rivers, wetlands, soils, litter, and moss habitats. They are able to live in both fresh and marine water, however, compared to naked amoeba, testate amoebae are less abundant in most soils. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Lousier''' | |||
and Parkinson, 1981 | |||
Revision as of 21:22, 22 April 2021
Definition
Testate amoebae (Testacea, or Hyalosphenia) are amoeboid protists, differing from naked amoebae in that they inhabit a test, or shell. The test of the testate can be created entirely by the amoeba, in which it would create an organic, siliceous, or calcareous shell depending on the species of testate amoeba. These tests created entirely by the amoeba are known as autogenic tests, as seen in figure 1. An xenogenic test is made up of particles of sediment collected by the amoeba which are then agglutinated together by secretions within the cell, as seen in figure 2.

Habitat
This group of free-living microorganisms inhabit aquatic to moist habitats including: estuaries, lakes, rivers, wetlands, soils, litter, and moss habitats. They are able to live in both fresh and marine water, however, compared to naked amoeba, testate amoebae are less abundant in most soils. They thrive in soil environments that are moist and within forested systems.
References
Lousier and Parkinson, 1981