Humus: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
'''Mull''' | '''Mull''' | ||
mull can be found in hardwood forests, deciduous forests, or grasslands in warm, humic climates. unlike mor, the pH in this humus formation is much higher and larger insects are more abundant. mull is subject to rapid decomposition and is well mixed with minerals | mull can be found in hardwood forests, deciduous forests, or grasslands in warm, humic climates. unlike mor, the pH in this humus formation is much higher and larger insects are more abundant. mull is subject to rapid decomposition and is well mixed with minerals | ||
[[File:mor_moder_mull_picture.gif]] | |||
'''Benefits of Humus''' | '''Benefits of Humus''' | ||
Revision as of 13:43, 19 April 2018
Humus
Humus is a type of soil created from decaying plants and organisms. Coined by a french soil scientist, Muller, the name is derived from the latin word "soil". Humus is difficult to describe is yet to be fully understood.
Description
Humus is a a non living organic matter in soil that is derived from microbial decomposition of plant and animal substances. Humus is dark colored and consists of approximately 60% carbon, 6% nitrogen and small amounts of sulfur and phosphorus.
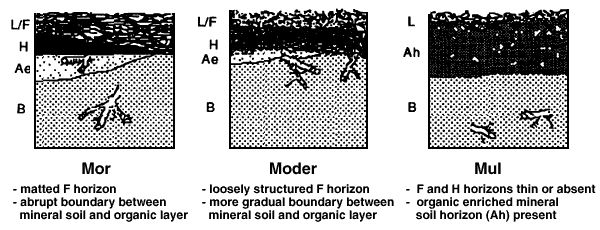
Formations of humus
Mor Mor is generally found in coniferous forests or mixed-wood forests. it is also associated with acidic conditions. mor comes fromcepomposing organic matter that lies on the surface of the soil. Fungi, earthworms, and small arthropods are some common organisms that decay into mor. Mor usually contains a low mineral content. The biological activity is relatively low.
moder Moder is the transitional form of humus. it lies between mull and moder. this humus is moderately humified and has characteristics of both mor and mull. moder can be found where mor or mull are not gereally favorable.
Mull
mull can be found in hardwood forests, deciduous forests, or grasslands in warm, humic climates. unlike mor, the pH in this humus formation is much higher and larger insects are more abundant. mull is subject to rapid decomposition and is well mixed with minerals
Benefits of Humus
humus absorbs moisture, therefore it raises the temperature of the soil and can maintain its heat. this can prevent the roots of plants form frosting during cold weather events. Humus holds onto nutrients and can prevent them from leaching. Humus can absorb moisture which can help soil during dry weather events. Since humus can retain nutrients, this allows plants and organisms to thrive in the soil. Humus can protect the soil from extreme temperatures.