Essential ecosystem services: Difference between revisions
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
'''S=f(cl,o,r,p,t,...)''' | '''S=f(cl,o,r,p,t,...)''' | ||
Soil=Formation(Climate, Organisms, Relief or Topography, Parent Material, Time, ...) [[File:soil-forming-factors.png|300px| | Soil=Formation(Climate, Organisms, Relief or Topography, Parent Material, Time, ...) [[File:soil-forming-factors.png|300px|thumb|-Ruth Heindel]] | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 21 March 2018
Ecosystem Services

Ecosystem Services are the documentation of the values and the benefits derived from ecosystems and the natural resources provided by the services. Ecosystem services are the benefits humans gain within marine and terrestrial ecology. For example, timber, clean water, food, and various cultural values. These services can be classified into four categories, provisioning services, regulating services, supporting services and cultural services.
Services of Ecosystems
Provisioning Services: These services provide the ecosystem and it's inhabitants with energy and material. They provide essential materials and energy through the output of productivity and these can be any types of useful resources, like food or water. An example of provisioning services would be the conditions an ecosystem has that allows it's inhabitants to be able to obtain food, whether this is from growing it, collecting it, hunting it, harvesting it, or from a plants perspective, producing it. The conditions an ecosystem may have would be the amount of rainfall per "wet" or "dry" season. This would directly affect the quality of soil of the ecosystem and thus affecting the type of flora and provisioning services within the ecosystem.
Regulating Services: Are the services that act as managers, maintaining the quality of air, soil, and other parts of an ecosystem. Regulating services also provide flood and disease control. An example of regulating services is Carbon Sequestration and storage. This occurs when trees and plants grow, they utilize and remove CO2 from the atmosphere. This regulates the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, provides an ecosystem with oxygen and manages change in temperature.
Supporting Services: Are the basis to all ecosystem services, they provide a place to live for plants and animals, while a strong diversity between plants and animals. An example of supporting services is maintenance of genetic diversity. This is how we conserve and protects unique species and maintain the diversity of species within an ecosystem. A large portion to maintenance of genetic diversity is documentation, because if a species is nearing what classifies as "Endangered," then action needs to be taken right away.
Cultural Services: Are the non-material benefits that humans gain from an ecosystem. This can be artistic and aesthetic inspiration, cultural identity, spiritual experiences with the natural environment and even a feeling of being at home. An example of cultural services is aesthetic and artistic appreciation. Art, culture and even science has been heavily influenced by biodiversity, natural landscapes, and ecosystems. Also, language, knowledge and our natural environment have been interconnected throughout the history of humans.


Example :Soil Formation
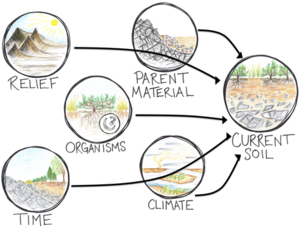
Soil is incredibly heterogeneous and varies from place to place. For example, it has different characteristics from country to country and even from town to town. An important factor to understanding soil formation, is understanding what parent material is. Parent material are rocks, that have been broken down, due to either physical, chemical or biological weathering. The important factor is that when there is parent material present, and along with dead organic matter, microorganisms, plants and animals, soil can be formed.
Hans Jenny, a major influence in soil ecology, coined the term "Pedogenesis" or soil formation. He furthered how we view soil formation and created an equation displaying factors of soil is formed and this equation is called the Jenny Equation:
S=f(cl,o,r,p,t,...)
Soil=Formation(Climate, Organisms, Relief or Topography, Parent Material, Time, ...)
Why is it important to humans, what benefits do we gain ?
Processes affecting soil formation
Factors that affect soil formation
Jenny equation are the factors
References
Wallace, Ken J. 2007 October. "Classification of Ecosystem Services: Problems and Solutions." https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006320707002765
Queensland Government. 2013. October 8. "How Soils Form." https://www.qld.gov.au/environment/land/soil/soil-explained/forms
http://www.ecosystemservicesseq.com.au/step-5-services/food
http://www.ecosystemservicesseq.com.au/step-3-functions/soil-formation
http://www.teebweb.org/resources/ecosystem-services/
http://www.fao.org/ecosystem-services-biodiversity/background/regulating-services/en/ http://www.fao.org/ecosystem-services-biodiversity/background/provisioning-services/en/
Picture References:
McClenaghan, David. "Bee Collecting Pollen." http://www.scienceimage.csiro.au/image/3822/bee-collecting-pollen/
Pan Xubin. "Diversity and Classification." http://www.bioedonline.org/slides/content-slides/diversity-and-classification/